Bile Acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase
| Bile Acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase | ||
|---|---|---|
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 418 amino acids | |
| Secondary to quaternary structure | Monomer | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene name | BAAT | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme classification | ||
| EC, category | 3.1.2.2 , transferase | |
| Response type | Transmission of cholic acid | |
| Substrate | Choloyl-CoA + glycine / taurine | |
| Products | Bile salts + CoA | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | multicellular animals | |
The bile acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase (BAT) is the enzyme in animals , the last step in the biosynthesis of bile salts catalyzed . Here is cholic or deoxycholic of CoA on amino acids transmitted in humans, these are up to 95% glycine or taurine . The reaction takes place in the peroxisomes of the liver cells ( hepatocytes ). The amidation increases the ability of the compounds to emulsify significantly, which means that lipids and vitamins can be better absorbed. Mutations in BAAT - gene are the cause of the rare Hypercholanämie (FHCA).
Catalyzed reactions
 + H 2 N-CH 2 -COO - ⇒
+ H 2 N-CH 2 -COO - ⇒ 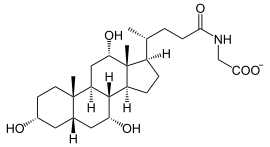 + CoA -SH
+ CoA -SH
Choloyl-CoA reacts with glycinate to form glycocholate and CoA-SH. Equivalent to this, the reaction with taurate to taurocholate takes place.
Individual evidence
Web links
Wikibooks: Biochemistry and Pathobiochemistry: Bile Acid Metabolism - Learning and Teaching Materials