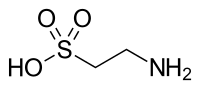
Taurine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Taurine | |||||||||||||||||||||
| other names | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 2 H 7 NO 3 S | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
monoclinic, colorless and odorless prisms |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 125.14 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.709 g cm −3 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
328 ° C (decomposition from 300 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Taurine or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid is an organic acid with one sulfonic acid and one amino group . Taurine is an aminosulfonic acid and not an aminocarboxylic acid and therefore cannot form peptides . However, it is produced in the metabolism as a breakdown product of the amino acid cysteine .
history
Taurine was isolated from the ox bile in 1827 by Leopold Gmelin and Friedrich Tiedemann and called bile asparagine . It is present in the bile as taurocholic acid , a cholic acid amide from which it can be released through acid hydrolysis . The term "taurine" comes from the Latin name for bull bile, Fel tauri , or from the Greek word tauros for "bull" and was first mentioned in 1838 in literature.
properties
Taurine is a colorless crystalline substance that decomposes above 300 ° C and melts at 328 ° C. It is soluble in water up to approx. 100 g / l . The good solubility in water and the high melting point can be explained - similar to amino acids - by the formation of the zwitterion (H 3 N + -C 2 H 4 -SO 3 - ).
Taurine is industrially addition of sulfite to aziridine made.
physiology
In the metabolism of adults, taurine is formed from the amino acid cysteine , which is oxidized in several intermediate steps while consuming oxygen and NAD + . A second path of development arises from the breakdown of coenzyme A by decarboxylation of cysteamine . Food intake is not necessary for adults.

It is assumed that the taurine content in the body of a healthy person weighing 70 kg is between 30 and 70 g, about 75% of which is in the muscle cells , the rest mainly in the brain, heart and blood. A healthy person has between 0.43 and 1 g of taurine per 1 kg of body weight in their body. Breast milk contains between 25 and 50 milligrams of taurine per liter.
Dogs can produce taurine themselves, cats produce only small amounts, so they have to take in taurine from food .
effect
The few clearly defined tasks of taurine in metabolism include the formation of bile acid conjugates , influencing signal transmission and the potential role in the development of the central nervous system and heart function. Taurine stimulates the influx and membrane binding of calcium . It also supports the movement of sodium and potassium across the cell membrane. The stabilization of the membrane potential supported by this shows an increase in the contraction and an anti- arrhythmic effect on the heart. Taurine is a powerful antioxidant and can protect tissues from oxidative damage. A low intramuscular taurine concentration is characteristic of chronic kidney failure . Taurine deficiency leads to disorders of the immune system in the human body .
In addition, animal experiments have shown that taurine has an anti-inflammatory effect. A depletion of taurine in the tissue pools, especially the lung tissue, leads to inflammation. Researchers at the University of London's School of Pharmacy found that taurine can reduce liver damage caused by alcohol . In a study with endurance athletes , no performance-enhancing effect could be demonstrated. A placebo effect is sometimes assumed.
In animal experiments with rats, taurine lowered blood pressure and, when administered with salt, led to life-threatening hypernatremia . It also accelerates the metabolism by influencing the insulin level, which could explain the strengthening effect of taurine in energy drinks , in which it is one of the main ingredients alongside caffeine and sugar. A can (250 ml) of the energy drink Red Bull contains z. B. 1 g taurine. The ability of taurine to influence the metabolism of insulin could not be confirmed in humans. There are indications that taurine should be given in cases of renal insufficiency and pneumonia . Other research seems to suggest that taurine-containing energy drinks should be avoided if you have kidney failure. The exogenous supply of taurine can also be useful in certain metabolic situations with cystic fibrosis . Other studies suggest that an additional taurine intake of 6 g of taurine per day over a period of one week can increase capacity during exercise.
Web links
- Michael Bretz: Taurine - chemistry, biochemistry, application (PDF; 130 kB). Institute for Pharmacy and Food Chemistry at Julius-Maximilians-Universität Würzburg , seminar paper, 43 pages (winter semester 2001/2002).
- Michael Bretz: The additives, structure and extraction of the additives in energy drinks (a seminar paper on energy drinks and what's behind them)
literature
- The use of taurine and D-glucurono-gamma-lactone as constituents of the so-called “energy” drinks . In: EFSA Journal . tape 7 , no. 2 , 2009, p. 935 , doi : 10.2903 / j.efsa.2009.935 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on TAURINE in the CosIng database of the EU Commission, accessed on May 11, 2020.
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on taurine. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on December 19, 2011.
- ↑ Beukes, JA; Mo, F .; van Beek, W .: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 9 (2007) 4709-4720.
- ↑ a b c Taurine data sheet from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on April 23, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on taurine in the ChemIDplus database of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM)
- ↑ EC number 1.13.11.20 (cysteine dioxygenase)
- ↑ EC number 4.1.1.29 (sulfinoalanine decarboxylase).
- ↑ EC number 1.8.1.3 (hypotaurine dehydrogenase).
- ↑ a b P. Fürst, H.-K. Biesalki among others: nutritional medicine. Thieme-Verlag, Stuttgart, 2004, p. 95.
- ↑ Schuller-Levis, GB and Park E. (2004): Taurine and its chloramine: modulators of immunity. In: Neurochem Res. Vol. 29, pp. 118-126. PMID 14992270 ; doi: 10.1023 / B: NERE.0000010440.37629.17 .
- ↑ Article on BBC News: The ultimate hangover cure? .
- ↑ EU.LEn-Spiegel 1995 / H. 1 / S. 6–7.
- ↑ Paul Benjamin Reszel: Tri-Knowledge: Taurine - Nothing precise is not known. Influence on performance. Article at Triathlon.de, accessed on August 20, 2010.
- ↑ EU.LEn-Spiegel 1996 / H. 5 / S. 9.
- ↑ AT Nandhini et al: Taurine modifies insulin signaling enzymes in the fructose-fed insulin resistant rats. In: Diabetes Metab 31, 2005, pp. 337-344. PMID 16369195 .
- ↑ Qualitative determination of taurine in Red Bull using the HPLC method .
- ↑ Brøns, Spohr, Storgaard, Dyerberg, Vaag: Effect of taurine treatment on insulin secretion and action, and on serum lipid levels in overweight men with a genetic predisposition for type II diabetes mellitus , PMID 15054439 .
- ↑ New human data for the evaluation of energy drinks (PDF; 125 kB).
- ↑ Astrid Wächtershäuser, Joachim G. Bargon, Jürgen Stein: Nutrition in cystic fibrosis. In: Ernähr-Umschau , Volume 49, No. 10, 2002, p. 383 ( online ).
- ↑ M. Zhang, I. Izumi, S. Kagamimori, S. Sokejima, T. Yamagami, Z. Liu, B. Qi: Role of taurine supplementation to prevent exercise-induced oxidative stress in healthy young men. In: Amino acids. Volume 26, Number 2, March 2004, pp. 203-207, doi: 10.1007 / s00726-003-0002-3 , PMID 15042451 .
