Counter-track indicator
The opposite track indicator (Zs 6) is a signal from the group of additional signals .
According to the signal book of Deutsche Bahn AG, its meaning is: The route leads into the main track against the normal direction of travel.
It is available as a light signal or a shape signal. The shape signal is only used if the main signal only allows routes to the opposite track.
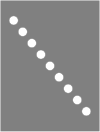
As a light signal, it has the following appearance: A white glowing oblique light strip, the ends of which are usually bent vertically up and down. DV 301: The ends cannot be angled until further notice.
As a shape signal: A rectangular black disc with a white border and a white stripe rising from right to left, the ends of which are angled vertically. The shape signal is reflective.
The signal used to be called track change indicator. The Eisenbahn-Signalordnung (ESO) contains this term to this day. In the area of the former German Federal Railroad, the signal screen of the opposite track indicator was covered with a diamond-shaped panel. Such indicators still exist today. They are often there individually behind the exit signals shortly before the start of the free route.
At the former Deutsche Reichsbahn the signal was called Zs 7 until the signal books were harmonized. The ends of the strip that are still not angled are created by using the WSSB additional display with five by nine light points. One lamp circuit can feed four or five lamps 12 V, 6/6 W. Two rows with ten light points are used for better visibility in new buildings. There are also no angled strips in electronic interlockings with Ks signals and additional displays in LED or light guide technology.
The operating procedure, which is constantly set up for driving on the opposite track with signal Zs 6, is called track changing mode .
In the area of the former Deutsche Reichsbahn, the counter-track indicators are usually attached to the main signal and are also used for the counter-track replacement signal ; in the network of the former Deutsche Bundesbahn, Zs 6 are often set up alone in front of the last track junction, which decides between regular and counter-track. As a result, the routes of several tracks should share an additional indicator. In interlockings with Ks signals, the substitute signal aspect for journeys to the opposite track is indicated by the combination of Zs 1 on the main signal and Zs 6 on the separate additional indicator.
The symbol of an opposite track indicator in safety-related plans consists of a white square with a black triangle in the upper left corner. This triangle should symbolize an arrow rising to the top left: "Top left" stands for the transition to the opposite track (schematic).
Individual evidence
- ↑ Deutsche Bahn AG: Guideline 819 "Planning LST Systems", Module 819.9002 "Symbols for Safety Plans"