Yellow wool pouch rat
| Yellow wool pouch rat | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Yellow woolly rat ( Caluromys philander ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Caluromys philander | ||||||||||||
| ( Linnaeus , 1758) |
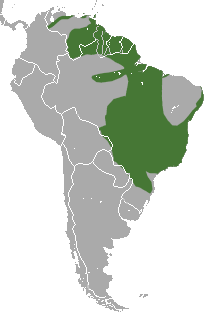
The yellow woolly rat ( Caluromys philander ) is widespread in tropical South America.
features
The animals reach a head trunk length of 16 to 28 cm, have a 25 to 40 cm long tail and reach a weight of 140 to 390 grams. The tail is usually 50% longer than the length of the head. On the back, on the sides of the body and on the outside of the limbs, the animals are light brown to yellow-brown or reddish-brown, sometimes mixed with gray tones. The belly is bright orange. The head is gray with a dark gray stripe on the muzzle and brownish rings around the eyes. The fur is dense and soft and usually shorter in populations that live in the lowlands and longer in animals from the mountainous regions. The prehensile tail is only hairy on the 10 to 20% of the tail length near the body. The hairless remainder is brownish, sometimes with light spots. The paws are hairless and light gray or whitish. The ears are light brown, the fur at the base of the ears is yellowish. The eyes are brownish with round black pupils. Females do not have a fully developed pouch, just deep abdominal folds that grow larger as pups are about to be born. The females have seven teats, one in the middle and three on each side.
habitat
The yellow woolly rat occurs in tropical lowland rainforests and in mountain forests up to heights of 1600 meters. It is more common in secondary forests than in primary forests . In dry forests in Bolivia or in the Brazilian Caatinga it occurs mainly in wetter areas. It is tree-dwelling and usually stays in the summit above a height of ten meters. If human settlements are near the forest, the yellow woolly rat can also be found in buildings, especially in the roof truss.
Way of life
Yellow woolly rats are nocturnal and rather solitary, but several specimens can be seen eating together in a tree. Males held in captivity together form hierarchies with a dominant animal even without females being present. The animals are tree-dwelling and rarely go to the ground. They rest in tree hollows, where they build nests out of leaves. The area inhabited by a single animal ranges in size from 0.3 ha to 8.9 ha. The territories overlap and are expanded during the dry season when the food supply is poor. Yellow wool pouch rats are common. In French Guiana up to 200 specimens can live in an area of 1 km², in Venezuela it is a maximum of 80 per 1 km².
nutrition
Like the other two species of pouch rats, and untypical of the pouch rats as a whole, yellow pouch rats feed mainly on fruits. The undigested seeds from the fruits can have a volume fraction of 75 to 90% in the excretions of the animals from rainforests. The fruits consumed include those of the palm genus Astrocaryum , those of ant trees ( Cecropia ), figs ( Ficus ), fruits of the mimosa family Inga and fruits of the passion flowers ( Passiflora ). The remainder of the diet consists mostly of invertebrates, including beetles, hymenoptera , arachnids, grasshoppers, butterflies, beaked peas and two-winged birds . Yellow woolly pouch rats play an important role in the spread of semen through their excretions. In the case of yellow woolen rats from drier regions, the proportion of insects in the food is higher overall. They mainly eat invertebrates during the dry season and more fruit in the rainy season. Blossoms and nectar as well as tree sap are also consumed.
Reproduction
Females get 2 to 7 young animals per litter. They are born in tree hollows or leaf nests between lianas. Man-made breeding caves are also used. The gestation period is around 21 days. After birth, the young suckle on the teats for a period of 75 to 80 days. After that, the female can leave the nest for the first time without the young. They are suckled for another 30 to 45 days and are completely independent about 130 days after their birth. In good, nutritious years, females can give birth three times. If food is scarce, there is only one litter a year.
Subspecies
A distinction is made between four subspecies, two of which may have to be classified as separate species, as they differ significantly from the nominate form morphologically and morphometrically :
- Caluromys philander philander , in Venezuela south of the Orinoco , in the three Guyanas and in northern Brazil east of the Rio Negro .
- Caluromys philander affinis , central and western Brazil ( Mato Grosso ) and adjacent areas of Bolivia.
- Caluromys philander dichurus , eastern and southeastern Brazil. Possibly a separate species.
- Caluromys philander trinitatis , Venezuela north of the Orinoco and Trinidad . Possibly a separate species.
supporting documents
- ↑ a b c d e f Diego Astúa: Family Didelphidae (Opossums). Pages 132-133 in Don E. Wilson , Russell A. Mittermeier : Handbook of the Mammals of the World - Volume 5. Monotremes and Marsupials. Lynx Editions, 2015, ISBN 978-84-96553-99-6
Web links
- Caluromys philander in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2015 Posted by: Brito, D., Astua de Moraes, D., Lev, D. Soriano, P. & Emmons, L., 2015. Accessed on 12 March 2018 .