Skin bleeding
As skin blood flow is called the blood outlet ( Erythrodiapedese ) of blood vessels in the skin or mucous membranes . The cause of skin bleeding can be an injury or an abnormally increased tendency to bleed . Fresh skin bleeding is indicated by a reddish discoloration of the skin. As the hemoglobin contained in the erythrocytes (red blood cells) is broken down, this color can change to brown, green and yellow over time.
Skin bleeding has two main causes:
- Damage in the endothelium
- Clotting disorders ( coagulopathies )
Depending on the type and size of the skin bleeding, different names are used in medicine :
| designation | size | definition | colour | shape | distribution | Pulsation | Response to pressure | Diseases | photo |
| Petechiae | up to pin head size | smallest punctiform skin or mucous membrane bleeding | fresh: reddish old: red-brown |
punctiform | scattered, mainly on the legs | No | cannot be pushed away | z. B. Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura |
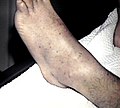
|
| Purpura | punctiform, small spots | spontaneous skin or mucous membrane bleeding (without trauma) | fresh: reddish old: red-brown |
hemorrhagic type papulonecrotic type polymorphic-nodular type |
preferably on the extensor legs, buttocks, arms, possibly generalized | No | cannot be pushed away | Allergic vasculitis , collagenosis , drug eruption |

|
| Ecchymosis and Sugillation | extensive sugillation up to approx. 30 mm |
extensive tissue bleeding | initially purple to bluish, later green-yellow and brown | round oval or irregular, possibly flat central elevation |
differently | No | No | Extravasation in the event of trauma or coagulopathy |

|
| Hematoma , horse kiss | large area | deep, massive bleeding in the tissues | initially purple to bluish, later green-yellow and brown | often raised | possible on the whole body | possibly painful | massive accumulation of blood in the skin and underlying tissues after trauma |

|
In addition to these terms, there are also the terms vibices (strip-like skin bleeding) and suffusions (extensive skin bleeding).
The erythema and roseoles are to be distinguished from this skin bleeding . These are temporary increased vessel fillings that can be pushed away with a glass spatula, for example.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b P. Fritsch: Dermatology, Venereology. 2nd edition, Verlag Springer, 2004, ISBN 3-540-00332-0 , p. 518. Restricted preview in the Google book search
- ↑ a b H. S. Füeßl, M. Middeke: Anamnesis and clinical examination. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2010, ISBN 3-131-26884-0 , p. 369. Limited preview in the Google book search