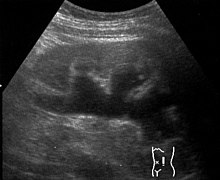
Hydronephrosis
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| N13.0 | Hydronephrosis in ureteropelvic obstruction |
| N13.1 | Hydronephrosis in ureteral stricture, not elsewhere classified |
| N13.2 | Hydronephrosis in obstruction due to kidney and ureteral stones |
| N13.3 | Other and unspecified hydronephrosis |
| N13.4 | Hydroureter |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |

A hydronephrosis ( water bag kidney , hydronephrosis ), or Uronephrose , is an extension of the renal hollow system , by a chronic urinary comes about and the medium by disturbance in the urine flow and long term destruction of kidney tissue is associated.
The urinary obstruction syndrome (or urinary obstruction syndrome) caused by obstruction of the drainage in the urethra, bladder, or ureters is known as hydronephrosis . If there are inflammatory changes, one speaks of a pyonephros or pyonephrosis .
Depending on the level of the disorder, not only the hollow kidney system, but also the ureter ( ureter ) can be sack-like as a hydroureter .
causes
The possible causes for the pressure increase in the renal system include:
- a mechanical restriction
- by problems within the Harnableitungssystems (ureter to external urethral orifice as Ureterabgangsstenosen , Ureterostiumstenosen , urethral , stone disease , prostatic hyperplasia , meatal stenosis , tumors )
- due to problems outside of the urinary drainage system ( tumors such as stage IIIb cervical cancer, retroperitoneal fibrosis , pregnancy , etc.)
- Malformations that lead to a backflow of urine into the kidneys, so the vesico-ureterorenal reflux . It is not uncommon to find malformations on the opposite side as well as other organs such as eyes , genitals , heart, etc.
- neuromuscular diseases with resulting neurogenic bladder emptying disorders , such as paraplegia , multiple sclerosis , spina bifida aperta , tabes dorsalis and others
- Drug abuse (e.g. ketamine )
- Disturbances of an unknown nature
One has to distinguish between unilateral and bilateral hydronephrosis. Only bilateral hydronephrosis leads to clinically significant renal insufficiency . Congenital, pronounced bilateral hydronephrosis of the fetus can become noticeable in the diagnosis of pregnancy through a reduced amount of amniotic fluid ( oligohydramnios ).
A distinction is to be made between the non-obstructive megacalicosis that does not require treatment .
Investigations
Examinations that are used to clarify hydronephrosis are sonography , intravenous pyelography , micturition cystourethrography, and scintigraphy (to assess residual kidney function).
In veterinary medicine, sonography and excretory urography are mainly used.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Günter Thiele (Ed.): Handlexikon der Medizin , Urban & Schwarzenberg , Munich, Vienna, Baltimore, Volume 2 (F − K), p. 1117.
- ↑ Joachim Frey : Clinic of diseases of the urinary tract. In: Ludwig Heilmeyer (ed.): Textbook of internal medicine. Springer-Verlag, Berlin / Göttingen / Heidelberg 1955; 2nd edition ibid. 1961, pp. 978-990, here: p. 998 ( Hydro- and Pyonephros ).
- ^ Street Ketamine-Associated Cystitis And Upper Urinary Tract Involvement: A New Clinical Entity
- ^ Harrison's Internal Medicine , 18th edition, Volume 3, McGraw-Hill , Berlin 2012, ISBN 978-3-940615-20-6 , p. 2593.
- ↑ Hubert Klein and Frauke Klein: Hydroureter and hydronephrosis in dogs. In: Kleintierpraxis 36 (1991), pp. 571-574.
Web links
- http://www.aerztekammer-hamburg.de/funktion/vortraege/pdfs/1024570160.pdf - Congenital hydronephrosis - current strategy of postnatal care (PDF file; 55 kB)
- Canine Hydronephrosis Pathology Image ( Cornell University )