Neurogenic bladder
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| N31.9 | Urinary bladder neuromuscular dysfunction, unspecified |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
Neurogenic bladder refers to a special form of bladder emptying disorder due to a disruption of the nerve supply (neurogenic) to the urinary bladder and / or the interplay of muscle contraction of the bladder wall and relaxation of the bladder sphincter . Usually there is damage to the spinal cord , more rarely damage to the nerve plexus in front of the sacrum ( lumbosacral plexus ).
distribution
The disease is congenital B. in meningomyeloceles .
The incidence of acquired bladder neurogenic disorder increases with age, more in women than in men.
pathology
Depending on the location of the underlying damage, a distinction can be made:
- above the brain stem :
- Overactivity of the detrusor
- Detrusor-sphincter dyssynergy
- obtained control of the emptying
- below Th6 :
- acute: spinal shock and atony
- Hyperreflexia with detrusor-sphincter dyssynergy
- above Th6 additional sphincter dyssynergy
-
Sacrum or lumbosacral plexus :
- Decreased detrusor activity
- increased bladder volume
- variable residual activity of the sphincter without dyssynergy
causes
Possible causes are all diseases that affect the motor and sensory nerve supply of the bladder and sphincter.
- Malformations of the spinal cord such as neural tube defects , syringomyelia , caudal regression syndrome
- Spinal cord injury
- disc prolapse
- poliomyelitis
- Brain tumors
- Disease of the peripheral nervous system e.g. B. in diabetes mellitus , alcoholism or vitamin B12 deficiency
- Neoplasms such as neuroblastoma or coccyx teratoma
- as a complication after operations such as anal atresia , closure of a spina bifida
Clinical manifestations
The continence is relevant for the patient and the care provider , in order to avoid complications it is essential to distinguish between
- increased bladder pressure with the risk of vesicorenal reflux if a barbed bladder develops
- flaccid sphincter with dripping urine
- flabby urinary bladder ( overflow bladder ) with risk of recurrent urinary tract infections
diagnosis
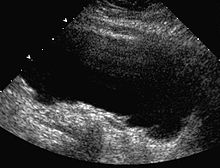
An important sign in imaging is the thickening of the bladder wall, especially trabeculation (irregular serration) of the wall. Ultrasound determination of residual urine , urodynamic examinations , and MCU are available for further clarification .
Differential diagnosis
The following must be distinguished: overactive bladder , dysfunctional micturition, benign prostatic hyperplasia , bladder tumors, bladder stones, infections such as acute cystitis .
therapy
Treatment consists of emptying the urinary bladder several times a day with a single-use catheter in order to avoid complications such as kidney damage from reflux and urinary tract infections. A botox injection is also a possible therapy for at least some of the patients.
literature
- W. Schuster, D. Färber (Ed.): Children's radiology. Imaging diagnostics. Vol. 2, p. 706, Springer 1996, ISBN 3-540-60224-0 .
- A. Sigel, R.-H. Ringert (Ed.): Pediatric urology. S. 172, Springer 2001, ISBN 978-3-662-08081-8 (print), ISBN 978-3-662-08080-1 (online).