INVEP
| INVEP
|
|
|---|---|

|
|
| Basic data
|
|
| developer | André Koppel Software GmbH, Berlin |
| Publishing year | 1999 |
| Current version | 3.1 |
| operating system | Linux, Windows, MacOS, iOS |
| programming language | C, ESQL / C, Perl, Mathematica, R |
| category | Industry software for lawyers, especially insolvency administrators |
| License | proprietary |
| German speaking | Yes |
| INVEP | |
INVEP ( acronym for In solvency Ve rwaltungs P rogram) is a business software for liquidator , restructurer and rehabilitator .
Development history
In 1994, the bankruptcy management system KoKa (KonkursKartei) was developed for the Berlin District Court . It was the first IT-supported system in Germany to manage bankruptcies , bankruptcies and court settlements. The program was programmed for a Sinix system and was in operation until January 1, 1999. The historical data of all bankruptcies since 1933 were entered into this system for research. A special feature of KOKA was the phonetic search system for person and company names. It led to a significant reduction in false negative reports, because names were found even if they were spelled differently.
From 1998 the court software KIKO was developed for the 1999 insolvency law. The development took place under LINUX, the system itself was operated under Solaris . X11 software for access was installed on the PC workstations . From January 1, 1999, when the new insolvency regulations came into force, KIKO was available at the Charlottenburg District Court and was in continuous use there at over 50 jobs until 2014. Since the current processes could not be imported into the successor system, KIKO has only been available for processing old processes and for historical research on 10 workstations since the successor system was put into operation (as of 2017).
The insolvency administrator software INVEP was created from the know-how in the development of these software systems. The software was initially only used in a limited number of insolvency administrator firms. Marketing started in 2004. INVEP has been the teaching standard for business law at Schmalkalden University since 2009 . The Schmalkalden University of Applied Sciences also offers further training to become a renovation manager, in which the software is an integral part.
Versions (selection)
| publication | Most important innovations |
|---|---|
| 1999 |
|
| 2003 |
|
| 2004 |
|
| 2007 |
|
| 2008 |
|
| 2010 |
|
| 2012 |
|
| 2013 |
|
| 2014 |
|
| 2015 |
|
| 2016 |
|
function
INVEP is an appliance for managing bankruptcies , for restructuring and reorganization. The software runs on a Linux system , the operator workstations can be Windows PCs, MACs or (mobile) iPADs . The system is operated in a virtualization environment ( VMWare , Hyper-V ). The installation includes INVEP modules, which can then be activated as required. The insolvency administrator software covers all areas of insolvency administration of consumer bankruptcies and regular bankruptcies . The various specialist areas such as table creation, receivables, address and appointment management are each extended with special functions that enable the management of even very large databases.
Technical and math challenges
In its various specialist areas, insolvency law contains very precise information on how certain calculations are to be carried out (e.g. in the quota calculation, i.e. for the money that is paid to the creditors or in the remuneration calculation). However, the legislature has generally disregarded the fact that a simple formula implementation does not work, since existing funds can only be offset to the nearest cents. However, this calculation that is accurate to the cent repeatedly leads to injustices in the range of fractions of a percentage. Such injustices or disadvantages can accumulate into visible orders of magnitude in the course of proceedings. However, this contradicts the principles of law. All corresponding INVEP calculation modules therefore contain suitable approximation and compensation methods (sometimes zero point searches) in order to compensate for disadvantages that have arisen.
In German insolvency law, there are almost no standards for forms. There are almost 100 different forms and printouts within insolvency proceedings, some of which have very different looks depending on the competent court or even the requirements of the Rechtspfleger. The design of basically the same forms can be so different between different courts that an expression generated for one court is rejected as formally incorrect by another court. Insolvency management systems such as INVEP therefore not only contain a large collection of forms, but also extensive customization options in order to respond to the wishes of clerks, courts and legal clerks. INVEP contains around 400 forms with more than 2,000 different forms. If necessary, the user can create his own forms.
In addition, the program system contains a large number of modules with which the quality of processing can be ensured. Such quality assurance measures are not only required by the professional associations ( GOI ), but also ensure that processing has been carried out in accordance with the law.
Challenges in user guidance
The business of insolvency processing is on the one hand a mass business, as there are always similar processes. On the other hand, there is an extremely high level of individual processing. Every process is different - even if certain processes are recurring. Often there are complex legal processes that are not even provided for by law (e.g. withdrawals of claims that have already been established). In particular, processes that are not legally standardized must be able to be recorded in a meaningful and consistent manner.
The entire processing of the case often takes place under immense time pressure, sometimes a large number of those involved in the procedure have to be recorded and written to in the shortest possible time (this results from the legally regulated deadlines). It has been shown that often very individual letters, which at the same time have to be generated in very large quantities, push every Office integration to its load limits. INVEP cannot solve these problems conclusively either, which is why the system contains two autonomous modules for generating the written work. Integrated into the system is an MS Office integration, which does not, however, generate maximum speed when generating several thousand letters. As an alternative, a LaTeX font generator is integrated, which is not as user-friendly as the Office connection, but which can itself generate tens of thousands of letters in a short time.
Module structure
The entire system consists of a large number of modules that can be dynamically expanded, configured and updated. The module structure is designed so that extensions, changes and updates can be imported during operation. This minimizes downtimes (e.g. for maintenance reasons). Basically, modules can be integrated in all programming languages supported by Linux. However, the manufacturer modules themselves are all programmed in C , ESQL / C, Perl , Mathematica and R. The basic or basic package contains all the modules for processing any number of insolvency proceedings of any size.
In the area of evaluations, analyzes and printouts, it is seldom necessary to actually create real new modules, since the majority of the forms and evaluations are in the form of XML and SQL structures and are processed by a graphical user interface . New analyzes and evaluations are therefore usually created in the form of new text control files (SQL and XML).
The INVEP.Basic package can be expanded with additional modules, e.g. B. through a creditor information system, personnel administration, controlling and much more
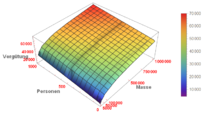
The financial analysis module INVEP.Quantum has existed since 2014 . It was originally developed for the detection of contestable facts and the determination of the time of insolvency. The analysis system enables the interactive three-dimensional visualization of financial data. This means that booking volumes with millions of data records can be clearly displayed. The CDF format is used to visualize the results in INVEP-Quantum . This means that only a Wolfram CDF player is required to view the results . Mathematical tools help to detect processes that remain undetected when bookings are viewed manually. In addition to its use in insolvency law firms, INVEP.Quantum is increasingly being used in business circles to support company valuations and to detect fraud. INVEP.Quantum has been offered as an independent product since 2015 .
Third-party extensions
Based on the defined interfaces, third-party providers can offer their own extensions that access the system independently. INVEP constantly monitors whether access is permitted in accordance with the assigned rights. For example, there is the option of connecting your own web server that visualizes the INVEP document management system as a media wiki and thus implements its own types of display and search via the access mechanisms integrated in INVEP.
Macro language
The program system contains its own macro language (OBAS), which - based on BASIC - facilitates the automation of recording processes. The programming language is active in all detection fields, when opening and closing screen masks and when pressing buttons. If necessary, it carries out calculations or evaluations, which are then automatically displayed or entered.
New functionalities are usually first implemented in INVEP in the form of extensions to the macro language. After the functions have been tested in this way, a mask and control system is added and the new functionality is also made available to the user in the form of new, menu-driven control modules.
In addition to the usual BASIC constructs, the language has been greatly expanded to include SQL, list, image processing and cryptography mechanisms. For example, it is possible to carry out automatic OCR processing of files scanned into the DMS with just a few lines of code:
res=ARCHIVE OCR(asnr;0) wordlist$=LIST WORDLIST$(TEXT FROM PDF$(res);0) words=LIST LEN(wordlist$) ad$="Anzahl Wörter: "&VAL$(words)
Software manufacturer
The software manufacturer is André Koppel Software GmbH , based in Berlin . André Koppel has been producing software for industry, research and selected sectors since 1980.
Awards
In 2013 INVEP received the IT Best of 2013 innovation award
In 2015, the software module INVEP.Quantum received the Wolfram Innovator Award 2015 from Wolfram Research for the only financial analysis software based on Wolfram Mathematica worldwide .
Trivia
KIKO is a recursive acronym and stands for "KIKO is not KOKA"
Web links
- INVEP homepage Website of the software
- Technology Conference INVEP.Quantum discussed at the Technology Conference in Champaign, Illinois, USA, on May 17, 2016
- Mathematica day in the WIAS Coverage analysis with INVEP and Mathematica presented and discussed in the Weierstrass Institute (WIAS), accessed on May 1, 2016
- ZInsO annual conference 2016 Discussion about software-supported company and risk analysis at the ZInsO annual conference, accessed on May 14, 2016
Individual evidence
- ↑ Berlin State Report | German EDV Court Day eV In: www.edvgt.de. Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ^ EDP country report Berlin. In: archiv.jura.uni-saarland.de. Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ H. Grote & M. Heyn: InsbürO - magazine for insolvency processing and debt relief procedures. (PDF) In: Carl Heymanns Verlag . P. 184f. , accessed on May 23, 2016 (5/2016).
- ↑ Use of the INVEP software. (No longer available online.) In: www.hs-schmalkalden.de. Archived from the original on April 22, 2016 ; accessed on May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ Reorganization Manager (FH) I Further training for insolvency administrators. In: www.hs-schmalkalden.de. Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ InsBüro 2005 Experience report: Increased efficiency and reduced costs through the introduction of INVEP ( Memento from May 6, 2016 in the Internet Archive )
- ↑ Article in Verlag CHBeck : Consideration and determination of the workload in insolvency proceedings , accessed on May 20, 2016.
- ↑ NZI Edition 23/2012: The Insolvency Statistics Act is here! (PDF). (PDF) Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ a b ZInsO edition 03/2017: Determination of the time of insolvency. (PDF) Retrieved January 31, 2017 .
- ↑ a b ZInsO issue 47/2016: Evidence in a digital world. (PDF) Retrieved November 25, 2016 .
- ↑ Big bankruptcy, big data (How insolvency administrators examine company bankruptcies with AI tools). Retrieved July 8, 2019 . c't 13/2019, p. 152ff.
- ↑ Description of OBAS for the use and application of OBAS (PDF). (PDF) Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ area42 - agency & system partner, http://www.area42.de/ : André Koppel Software: Specialists for realtime software and embedded systems. In: www.akso.de. Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
- ^ Huber Verlag für Neue Medien GmbH: Prize for the new INVEP module. (No longer available online.) In: www.aktiv-verzeichnis.de. Archived from the original on May 31, 2016 ; accessed on May 20, 2016 .
- ↑ Wolfram Innovator Award: Wolfram Technology Conference. In: www.wolfram.com. Retrieved May 20, 2016 .
Coordinates: 52 ° 25 ′ 25.3 ″ N , 13 ° 16 ′ 3.7 ″ E