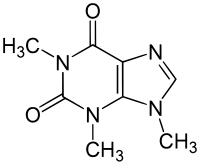
Isocaffeine
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Isocaffeine | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 194.19 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
286 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Isocaffeine (1,3,9-trimethylxanthine) is a chemical compound which differs from caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine) only in the position of a methyl group . This changes the external structure of the molecule and the pharmacological effect is therefore significantly different from that of caffeine.
Isocaffeine has a much weaker effect, the muscle rigidity remains and the tetanic phenomena take a back seat to the paralysis. In contrast to caffeine, isocaffeine has only a weak diuretic effect .
It is an adenosine receptor antagonist .
properties
Isocaffeine crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system in the space group P 2 1 / n (space group no. 14, position 2) with the lattice parameters a = 771.7 pm , b = 791.5 pm, c = 1364.6 pm and β = 92 , 86 °. In the unit cell contains four formula units .
literature
- B. FRÄNKEL: "The drug synthesis based on the relationships between chemical structure and effect" , FIFTH, REVISED EDITION, BERLIN, PUBLISHING JULIUS SPRINGER 1921
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d data sheet 1,3,9-trimethylxanthine from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 11, 2011 ( PDF ).
- ^ H. Rasmussen, E. Sletten: "The Crystal and Electronic Structure of Isocaffeine, (1,3,9-Trimethyl-2,6-dioxypurine)" , in: Acta Chem. Scand. , 1973 , 27 , pp. 2757-2768. (PDF; 1.1 MB)