Levosimendan
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
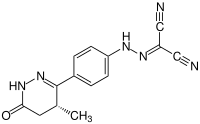
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Levosimendan | ||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 14 H 12 N 6 O | ||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Drug information | |||||||||||||||||||
| ATC code | |||||||||||||||||||
| Drug class |
Calcium sensitizer |
||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 280.28 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
210-214 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Levosimendan (trade name Simdax ; Orion Oyj ) is a drug from the calcium sensitizer group , which is used in the short-term treatment of acute decompensated, severe chronic heart failure .
Clinical information
Application areas (indications)
Levosimendan is indicated for short term treatment of acutely decompensated , severe chronic heart failure (English: acutely decompensated severe chronic heart failure , ADHF) in situations where conventional therapy with intravenous diuretics is not sufficient and treatment with inotropic acting substances suitable appear.
Dosis, kind and Time of the Use
Levosimendan is used as a concentrate for solution for infusion, which must be diluted before administration. It is only intended for use in hospitals and requires adequate monitoring equipment and experience in therapy with inotropes. The dose and duration of treatment should be individually adjusted according to the patient's clinical condition and response to treatment.
Contraindications (contraindications)
Levosimendan should not be used in:
- severe hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Racing heart ( tachycardia )
- significant mechanical obstructions affecting ventricular filling, ventricular outflow, or both (e.g. aortic stenosis )
- severely impaired liver or kidney function
- Torsade de pointes
Adverse effects (side effects)
The most common side effects observed were abnormally fast heartbeat, drop in blood pressure and headache. Insomnia, dizziness , gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea) and low potassium and hemoglobin levels were also common.
Pharmacological properties
Levosimendan increases the pumping power of the heart (positive inotropic effect) and dilates the blood vessels (vasodilatory effect). The blood flow to the heart muscle is improved without consuming more oxygen.
Mechanism of action (pharmacodynamics)
Levosimendan increases the calcium sensitivity of contractile proteins by binding to the cardiac troponin C is caused. It thus increases the impact force (positive inotropic effect), but does not impair diastolic relaxation, which is attributed to the fact that the transmembrane calcium current is not increased above pharmacologically relevant concentrations. In certain patients positive lusitropia could even be demonstrated by levosimendan, which may be due to the fact that levosimendan only binds to troponin C in the calcium-rich phase of the systole and dissolves again in the calcium-poor diastole and has no effect. Levosimendan also opens ATP- sensitive potassium channels in the smooth vascular muscles, which reduces the vascular resistance in the coronary arteries and in the systemic (arterial and venous) vessels ( vasodilatory effect). The heart's preload and afterload are reduced.
Levosimendan thus belongs to the group of inodilators .
Pharmacokinetics
Levosimendan is almost completely metabolised in the liver , 54% of the dose is excreted in the kidneys and 44% in the faeces . The half-life is about 1 hour. The hemodynamic effect that persists for about 7 to 9 days after discontinuation of levosimendan is due to the metabolites (OR-1855 and OR-1896), which have half-lives of 70 to 80 hours.
Other Information
Simdax was approved in Sweden in 2000 as the first country in the world, followed by approval in other European countries in 2001 and in Germany and Switzerland in 2013. The drug was developed by the Finnish company Orion.
A randomized, double-blind, multicenter study investigated the influence of levosimendan on patients after heart surgery with acute left heart failure and requiring catecholamines. The patients received levosimendan or placebo in addition to catecholamine therapy. The study was terminated after the enrollment of 506 patients and published in 2017 because there was no significant benefit from the addition of levosimendan.
See also
Individual evidence
- ^ The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals , 14th Edition (Merck & Co., Inc.), Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2006; P. 948, ISBN 978-0-911910-00-1 .
- ↑ There is not yet a harmonized classification for this substance . A label of (-) - (R) - [[4- (1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-4-methyl-6-oxo-3-pyridazinyl) phenyl] hydrazono] is shown, which is derived from a self-classification by the distributor propane-dinitrile in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on July 7, 2020.
- ↑ Swedish professional information Simdax, as of July of 2009.
- ↑ K. Jorgensen, O. Bech-Hanssen, E. Houltz, S.-E. Ricksten: Effects of Levosimendan on Left Ventricular Relaxation and Early Filling at Maintained Preload and Afterload Conditions After Aortic Valve Replacement for Aortic Stenosis. In: Circulation. 117, 2008, pp. 1075-1081, doi : 10.1161 / CIRCULATIONAHA.107.722868 .
- ↑ Giovanni Landoni, Vladimir V. Lomivorotov, Gabriele Alvaro, Rosetta Lobreglio, Antonio Pisano et al .: levosimendan for Hemodynamic Support after Cardiac Surgery. N Engl J Med 2017; 376: 2021-2031May 25, 2017, PMID 28320259 .