M901
| M901 ITV | |
|---|---|

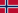
M901 ITV during the REFORGER '85 maneuver |
|
| General properties | |
| crew | 4 (commander, driver, two loaders) |
| length | 4.86 m |
| width | 2.70 m |
| height | 2.91 m (tower retracted, in marching position) 3.41 m (tower extended) |
| Dimensions | 12.5 tons |
| Armor and armament | |
| Armor | 38 mm frontal armor |
| Main armament | Twin starters for BGM-71-TOW anti-tank missiles |
| Secondary armament | 1 × 7.62mm machine gun; Smoke throwing system |
| agility | |
| drive |
General Motors 6V53, 6-cylinder, two-stroke diesel engine 212 HP (158 kW) |
| suspension | Torsion bar |
| Top speed | 64 km / h |
| Power / weight | 17.0 hp / ton |
| Range | approx. 480 km (road) |
The M901 ITV (ITV stands for I mproved T OW V ehicle ) is an anti-tank vehicle developed in the United States in the 1970s based on a modified M113 A1 chassis, which uses TOW anti-tank missiles made in the USA. The system was developed by the US conglomerate Emerson Electric Company .
History of origin
The M901, which entered service with the US Army in 1978 , was developed in response to the growing number of Warsaw Pact tanks in Eastern Europe . The M113 A1, which has proven itself in various missions, was equipped with the TOW anti-tank guided weapons delivered to the US armed forces in 1970 , which offered a high probability of kill . The group leader had a field of view of 270 ° with his periscope . The lowerable tower starter is capable of day and night combat. It has a side adjustment range of 360 ° and an elevation adjustment range of + 35 ° to −30 °. The M27 tower with the characteristic “hammerhead” attachment (M220 starter system ) contains the two TOW starter tubes that have to be loaded manually. The ammunition supply carried is a total of 12 missiles, ten of which are stowed in the tank and two in the launch tubes. In principle, all TOW variants can be used. The combat range for the TOW-2B version is 4500 m. A 7.62 mm machine gun is available as secondary armament . The tank destroyer is equipped with a thermal imaging device and a laser range finder.
Production ran from 1977 to 1998. During this period, 3315 units were manufactured for the US Army and other armed forces. The M901 ITV was procured by several NATO and Middle Eastern countries . The largest operators are currently Egypt and Greece, the last buyer to date is Thailand. In the US Army, the retirement took place after 15 years of service at the beginning of the 1990s. And that although with the M901 during Desert Storm at least 14 kills were recorded without losses . More modern vehicles like the M2 / M3 Bradley or the M1134 ATGM replaced the M901.
variants
- M901 : Use of the starting system M220A1 TOW.
- M901A1 : Use of the M220A2 TOW 2 starting system.
- M901A3 : Use of the M220A2 TOW 2 starting system based on the M113A3.
Users

-
 Bahrain : 38 units (used) received in 2000.
Bahrain : 38 units (used) received in 2000. -
 Egypt : 52 units received in 1983 and 130 used vehicles in 1995.
Egypt : 52 units received in 1983 and 130 used vehicles in 1995. -
 Greece : 24 units received in 1986 and 160 used vehicles in 1995/1996.
Greece : 24 units received in 1986 and 160 used vehicles in 1995/1996. -
 Israel : 450 units (used) received in 1995.
Israel : 450 units (used) received in 1995. -
 Jordan : 50 units received in 1980 and 23 used vehicles in 2000.
Jordan : 50 units received in 1980 and 23 used vehicles in 2000. -
 Kuwait : 56 units received in 1985 with 4840 BGM-71C-I-TOW missiles. In the second Gulf War , some M901 to have been captured by the Iraqi army.
Kuwait : 56 units received in 1985 with 4840 BGM-71C-I-TOW missiles. In the second Gulf War , some M901 to have been captured by the Iraqi army. -
 Morocco : 23 used units received in 1999.
Morocco : 23 used units received in 1999. -
 Norway : 126 units received in 1996, rebuilt on site.
Norway : 126 units received in 1996, rebuilt on site. -
 Pakistan : 24 units received in 1985.
Pakistan : 24 units received in 1985. -
 Portugal : 25 used units received in 1994.
Portugal : 25 used units received in 1994. -
 Thailand : 18 units received in 1997.
Thailand : 18 units received in 1997. -
 United States : Retired in the early 1990s and mostly sold to other states or given to museums.
United States : Retired in the early 1990s and mostly sold to other states or given to museums.
See also
Web links
- FAS.org - M901 Improved TOW Vehicle (English)
- GlobalSecurity.org - M901 Improved TOW Vehicle (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d M901 Improved TOW Vehicle M901A1 (English)
- ↑ inetres.com: USA - M901 Improved TOW Vehicle (English)
- ↑ a b c d M901 Improved TOW Vehicle (ITV) (English)
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j k SIPRI - Trade Registers USA (English)
- ^ Yves Debay: Operation Iraqi Freedom: Victory in Baghdad (= Special Obs 27). Concord Publication, 2003, ISBN 962-361-067-X , p. 50.

