Thioacetals
| Thioacetals |
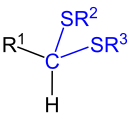
| Monothioacetals. Here, R 2 and R 3 are organyl residues (alkyl residues, aryl residues, arylalkyl residues, etc.), but not a hydrogen atom. R 1 can be an organyl radical (alkyl radical, aryl radical, arylalkyl radical, etc.) or a hydrogen atom. |
| Dithioacetals. Here, R 2 and R 3 are organyl residues (alkyl residues, aryl residues, arylalkyl residues, etc.), but not a hydrogen atom. R 1 can be an organyl radical (alkyl radical, aryl radical, arylalkyl radical, etc.) or a hydrogen atom. |
Thioacetals are chemical compounds that are derived from aldehydes and instead of the carbonyl group (a) two sulfanyl groups (-SR 1 and -SR 2 ) or (b) one sulfanyl group (-SR 1 ) and one alkoxy group or aryloxy group ( –OR 2 ), which are bound to the same carbon atom. They are geminally arranged sulfur analogues of diethers .
Originally, a distinction was made between the thioacetals formed from aldehydes (with one hydrogen atom) and the analogous compounds formed from ketones , the so-called thioketals . Nowadays, thioketals are also mostly regarded as a subclass of the thioacetals.
When thioacetals are formed from aldehydes or ketones and thiols , the intermediate products are the hemi- or monothio-hemiacetals [R ' 2 C (SR) (OH)], which can only be isolated in some cases.
synthesis
Dithioacetals are formed in the reaction of aldehydes (example: acetaldehyde ) and mono- or di- valent thiols (example: 1,3-propanedithiol ) with elimination of water. As a rule, this condensation reaction is carried out with acid catalysis.
Dithioacetals as protecting groups
In synthetic chemistry, dithioacetals are often used as protective groups for carbonyl groups of aldehydes or ketones.
In the Corey-Seebach reaction , dithioacetals serve as intermediates for the synthesis of asymmetrical ketones from aldehydes.
Related links
S , N -acetals
If the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone is reacted with a 1,2-aminothiol with elimination of water, an S , N -acetal is formed. Thiazolidines and 3- thiazolines are examples of heterocyclic S , N acetals.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 6: T-Z. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1988, ISBN 3-440-04516-1 , p. 4236.