Dioxoboric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
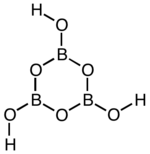
|
||||||||||||||||
| Simplified representation of the structure that is present in the first form | ||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Dioxoboric acid | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | HBO 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 43.82 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
|
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in water |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Dioxoboric acid is a chemical compound from the group of acids . Formally, it can also be assigned to the boroxine group of substances .
Extraction and presentation
Dioxoboric acid can be obtained by heating boric acid to 100 to 150 ° C. The third form arises, with boric acid generally not yet converted in addition to its crystals. If it is heated for too long, the second modification also occurs.
properties
Dioxoboric acid is a colorless solid that exists in three modifications and dissolves in water to form orthoboric acid. The conversion of the third form into the second form occurs rapidly at 160 ° C. By further heating to 160 ° C and higher, this finally changes into the first modification. At more than 500 ° C it decomposes into boron trioxide. The third modification crystallizes orthorhombically (a = 801.5 pm, b = 967.9 pm, c = 624.4 pm) with the space group Pnma (space group no.62 ) , the second monoclinic (a = 712.2 pm, b = 884.2 pm, c = 677.1 pm, β = 93.26 °) with the space group P 2 1 / c (No. 14) and the first cubic (a = 888.6 pm) with the space group P. 4 3 n (No. 218) . In the planar boroxine ring of the first form (HBO 2 ) n and its salts there are (pp) π bonds. The bond distances are between those of single and double bonds. In the second and third form, the boroxine rings are linked to one another via oxygen atoms, the second form being linked in a chain and the third form being linked three-dimensionally. The β-metaboric acid is thus composed of endless zigzag chains with the composition [B 3 O 4 (OH) (OH 2 )] n .
Individual evidence
- ^ A b c Jean d'Ans, Ellen Lax, Roger Blachnik: Pocket book for chemists and physicists . Springer DE, 1998, ISBN 3-642-58842-5 , pp. 316 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i j Georg Brauer (Ed.), With the collaboration of Marianne Baudler u. a .: Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 3rd, revised edition. Volume I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6 , p. 808.
- ^ William M. Haynes: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 93rd Edition . CRC Press, 2012, ISBN 1-4398-8049-2 , pp. 4–53 ( limited preview in Google Book Search).
- ↑ a b Data sheet Metaboric acid 99% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 22, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b Erwin Riedel, Christoph Janiak: Inorganische Chemie . Walter de Gruyter, 2011, ISBN 3-11-022567-0 , p. 582 ( limited preview in Google Book search).


