Monocrotaline
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
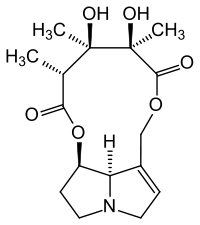
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Monocrotaline | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Crotaline |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 16 H 23 NO 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 325.36 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
204 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Monocrotaline is an alkaloid and, due to its structure, belongs to the group of pyrrolizidine alkaloids . It is of vegetable origin and poisonous.
Occurrence
Monocrotaline occurs in some species of the genus Crotalaria ( butterflies ); for example in the seeds of Crotalaria spectabilis and Crotalaria mucronata . There it serves to ward off predators, but it can also poison farm animals such as cattle.
The larvae of the butterfly Utetheisa ornatrix from the bear moth family feed almost exclusively on Crotalaria seeds and accumulate monocrotaline in their bodies. In this way, they are protected from predators such as spiders for the rest of their life (even after pupation as a butterfly).
structure
Monocrotaline is one of the retronecines and forms an eleven-membered macrocycle from the necine backbone and variously substituted pentanedioic acids . Further examples of the 30 or so known representatives of this structural pattern are Spectabilin and Grahamin .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f Data sheet Monocrotaline, analytical standard at Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on June 4, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ↑ Entry on monocrotaline. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on June 4, 2017.


