Nasal septum


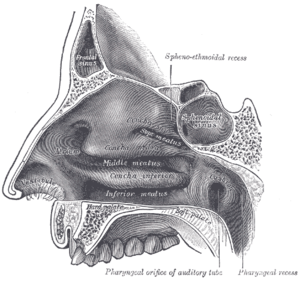
The nasal septum ( Latin septum nasi , German often also nasal septum ) is the middle partition of the nose . It consists of the membranous pars membranacea , the nasal septum cartilage ( Cartilago septi nasi ), an upper bony part of the ethmoid bone ( Lamina perpendicularis ossis ethmoidalis ) and a lower bony part, the ploughshare bone ( vomer ). In the anterior area of the nasal septum there is a network of blood vessels, the Kiesselbachi locus .
The nasal septum delimits the two nasal cavities . It is located in a bony guide groove in the upper jaw median in the nasal cavity and can deviate more or less from the midline. Due to its anatomical structure, the nasal septum, together with the nasal walls on the side and the two main nasal cavities, ensure optimal air circulation. In addition, the bony part of the nasal septum ensures a stable nasal framework and thus prevents the cartilaginous structures from collapsing. In the area of the transition between nasal cartilage and ploughshare, the nasal septum is thickened, which can lead to an obstruction of nasal breathing, especially in adults.
clinic
Nasal septum in a frontal CT image, the septum is shown in the middle, each lateral u. a. the conchae nasales, meatus nasi
If there is bleeding into the nasal septum, e.g. B. as a result of a nasal bone fracture, a septal hematoma forms . If you hit the nose, the cartilaginous part of the nasal septum can slide out of its bony guide groove (subluxation).
A deviation from the midline (lateral displacement, deformation) is known as a septal deviation (curvature of the nasal septum). It occurs in a large number of people and usually leads to asymmetrical flow conditions in both halves of the nose when inhaling and to noises when exhaling. This may mean that nasal breathing is obstructed and, depending on the location, can cause or massively increase snoring. A surgical correction is uncomplicated.
surgery
It is called septoplasty or septum resection in ENT medical terminology . The procedure takes place through the nostrils. The wrongly positioned cartilage or bone of the nasal septum is straightened and placed in the middle, working under the nasal mucosa. In most cases, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. It can also be done under local anesthesia. After the procedure, tamponade is placed in both nasal passages to stop the bleeding and fix the nasal septum in the middle. This will be renewed or removed by the doctor after a few days.
literature
- Ernst Mutschler , Hans-Georg Schaible, Peter Vaupel : Human anatomy, physiology, pathophysiology. 6th, completely revised and expanded edition. Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft, Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-8047-2342-9 .
- Franz-Viktor Salomon: respiratory system. In: Franz-Viktor Salomon, Hans Geyer, Uwe Gille (Ed.): Anatomy for veterinary medicine. 2nd, revised and expanded edition. Enke, Stuttgart 2008, ISBN 978-3-8304-1075-1 , pp. 324-367.


