Neotyphodium
| Neotyphodium | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
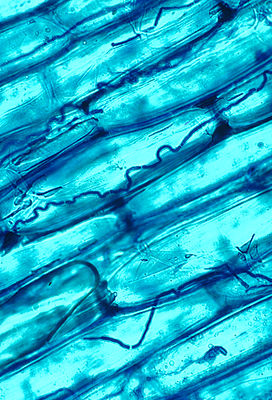
Mycelium of Neotyphodium coenophialum between leaf cells of the reed fescue |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Neotyphodium | ||||||||||||
| Glenn , CW Bacon & Hanlin | ||||||||||||
| species | ||||||||||||
|
Neotyphodium is a genus of fungus from the family of ergot fungus relatives (Clavicipitaceae). They are symbionts that live endophytically in various sweet grasses from the subfamily Pooideae and help protect the host plant from eating. Neotyphodium species reproduce exclusively asexually. The genus Neotyphodium is evolutionarily derived from the genus Epichloë , to which, with the exception of the lack of a sexual cycle, there are very great similarities.
features
The representatives of the genus Neotyphodium are endophytic fungi that live in the intercellular spaces of the leaves and stems of the host plants and form a constitutive symbiotic community with them. Spores and parts of the mycelium also occur in the seeds of the host plants, so that the fungus is passed on from the parent plant to the next generation.
The symbiosis consists on the one hand in the supply of the fungus with nutrients by the host plant. In return, the fungus protects the host plant against predators such as insects , herbivorous vertebrates and root-knot nematodes by producing alkaloids . In addition, the fungus improves the host plant's resistance to drought and controls its root growth.
The alkaloids produced by the representatives of the genus Neotyphodium include ergot alkaloids , in particular ergovalin and numerous clavins , loline alkaloids , lolitrems and the guanidinium alkaloid peramine . While loline alkaloids and peramin are responsible for the insecticidal effect, the neurotoxic lolitrems have an effect on vertebrates. Grazing cattle, which consume grass infected with Neotyphodium , are particularly affected by this effect . The ergot alkaloids produced by Neotyphodium species also have a predominantly toxic effect on vertebrates . The symptoms caused by ergot alkaloids in grazing cattle include weight loss, circulatory disorders, and disorders of reproductive capacity and lactation .
Systematics
The anamorphic genus Neotyphodium is very closely related to the teleomorphic genus Epichloë . Apart from the absence or presence of the sexual cycle, the representatives of both genera are similar in their characteristics. Neotyphodium species evolve from representatives of the genus Epichloë . They are derived from individual representatives of the genus Epichloë or from hybrids of at least two Epichloë species.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b C. L. Schardl, A. Leuchtmann, MJ Spiering: Symbioses of grasses with seedborne fungal endophytes . In: Annu Rev Plant Biol . 55, 2004, pp. 315-340. doi : 10.1146 / annurev.arplant.55.031903.141735 . PMID 15377223 .
- ^ LP Bush, HH Wilkinson, CL Schardl: Bioprotective Alkaloids of Grass-Fungal Endophyte Symbioses . In: Plant Physiol. . 114, No. 1, May 1997, pp. 1-7. ISSN 1532-2548 . PMID 12223685 .
- ↑ HF Tsai, JS Liu, C. Staben, MJ Christensen, GC Latch, MR Siegel, CL Schardl: Evolutionary diversification of fungal endophytes of tall fescue grass by hybridization with Epichloë species . In: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA . 91, No. 7, 1994, pp. 2542-2546. PMID 8172623 .
- ^ CD Moon, KD Craven, A. Leuchtmann, SL Clement, CL Schardl: Prevalence of interspecific hybrids amongst asexual fungal endophytes of grasses . In: Mol. Ecol. . 13, No. 6, 2004, pp. 1455-1467. doi : 10.1111 / j.1365-294X.2004.02138.x . PMID 15140090 .
