Oxocarbons
The term oxocarbons is used to denote different groups of chemical compounds according to different definitions .
After IUPAC definition (are among the Oxokohlenstoffen English oxocarbons ) all compounds consisting exclusively of carbon and oxygen are built. These are referred to in German as carbon oxides and include, for example, carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), carbon trioxide (CO 3 ), carbon suboxide (C 3 O 2 ), and mellitic anhydride ( dodecacarbon nonaoxide , C 12 O 9 ).
However, the term oxocarbons was coined earlier by Robert West for cyclic compounds of interconnected carbonyl groups , which can also be hydrated .
Oxocarbons to West
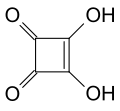
This group includes triangular acid , squaric acid , croconic acid and rhodizonic acid , which can be seen as the basic structure of this group with three to six carbonyl groups in the ring and the general formula C n O n H 2 (n = 3 to 6). A number of derivatives , in particular esters and salts, are also known.
history
Leopold Gmelin succeeded in producing croconic acid for the first time in 1825 by heating potassium carbonate with carbon in an iron retort . In doing so, he received a yellow substance as a by-product, which he called croconate potassium with the formula K 2 C 5 O 5 . After adding sulfuric acid , he was able to isolate the free croconic acid. In addition, Gmelin was able to observe a red substance that was designated by JF Heller in 1837 as potassium rhodizonate with the formula K 2 C 6 O 6 and from which he obtained the free rhodizonic acid after treatment with an acid. A few years later, Justus von Liebig found that potassium croconate and potassium rhodizonate could be synthesized by reacting carbon monoxide with potassium . The synthesis of triangular acid and squaric acid was only possible from the middle of the 20th century.
Manufacturing
In addition to the historical processes, there are now the following synthesis options:
- Triangular acid : reaction of dichlorocarbene with bis- tert -butoxyacetylene via triangular acid- bis- tert - butyl ester
- Squaric acid : dimerization of chlorotrifluoroethene and subsequent hydrolysis; intramolecular cycloaddition of hexachloro-1,3-butadiene and subsequent hydrolysis; electrochemical tetramerization of carbon monoxide
- Rhodizonic acid : trimerization of glyoxal
properties
The compounds are crystalline solids, the color of which increases from colorless to red as the ring size increases. They have a high acidity , with squaric acid being the strongest. The alkali metal salts of the acids are stable in the air and easily soluble in water. The oxo carbons can be with oxidizing agents such. B. easily convert nitric acid into corresponding polyhydroxy compounds. For example, dodecahydroxycyclohexane is obtained from rhodizonic acid and octahydroxycyclobutane from squaric acid.
Pseudooxo carbons
Under Pseudooxokohlenstoffen are compounds in which the oxygen atoms of oxocarbons are replaced by other atoms such as chlorine, nitrogen, or sulfur atoms (Thiooxokohlenstoffe) or atomic groups.
literature
- Arthur H. Schmidt: Oxocarbons. In: Chemistry in Our Time . 16th year 1982, No. 2, pp. 57-67, doi : 10.1002 / ciuz.19820160205 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Entry on oxocarbons . In: IUPAC Compendium of Chemical Terminology (the “Gold Book”) . doi : 10.1351 / goldbook.O04375 Version: 2.3.3.
- ^ Robert West, David L. Powell: New Aromatic Anions. III. Molecular Orbital Calculations on Oxygenated Anions , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1963 , 85 (17), pp. 2577-2579; doi : 10.1021 / ja00900a010 .
- ^ Robert West, Joseph Niu: Oxocarbons and their reactions . In: J. Zabicky (Ed.): The Carbonyl Group: Volume 2 (1970), p. 214. doi : 10.1002 / 9780470771228.ch4 .
- ↑ Joh. Florian Heller: About rhodizonic acid, a new oxidation stage of carbon, and croconic acid, then the salts of both. Prague, 1837 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ^ David Eggerding, Robert West: Synthesis and properties of deltic acid (dihydroxycyclopropenone) and the deltate ion . In: J. American Chemical Society, 1976, 98, pp. 3641-3644. doi : 10.1021 / ja00428a043 .
- ↑ JD Park, S. Cohen, JR Lacher: Hydrolysis Reactions of Halogenated Cyclobutene Ethers: Synthesis of Diketocyclobutenediol . In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1962, 84, pp. 2919-2922 doi : 10.1021 / ja00874a015 .
- ↑ Gunther Seitz: Pseudooxocarbons . In: Nachr. Chem. Tech. Lab. tape 28 , no. 11 , 1980, pp. 804-807 , doi : 10.1002 / nadc.19800281108 .