Paecilomyces variotii
| Paecilomyces variotii | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
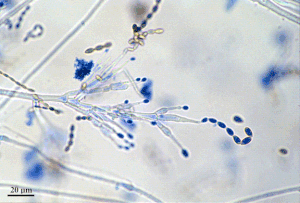
Paecilomyces variotii |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Paecilomyces variotii | ||||||||||||
| Bainier |
Paecilomyces variotii is a widespread mold described in 1907. It is an important pathogen for mold infections.
Paecilomyces variotii is often isolated from more heated substrates such as compost. It is also called a thermophilic mold because it can still grow at 50 to 60 ° C. It is able to colonize extreme locations and can even be resistant to preservatives such as sorbic , benzoic or propionic acid .
In its microscopic appearance, Paecilomyces is very reminiscent of Penicillium species. However, due to the very different risk potentials, these molds must not be confused. Penicillium species are predominantly green, and Paecilomyces variotii is more yellowish-brown.
Web links
Commons : Paecilomyces variotii - collection of images, videos and audio files
Individual evidence
- ↑ Paecilomyces variotii . schimmel-schimmelpilze.de; Retrieved August 31, 2010