Palladium (II) acetate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
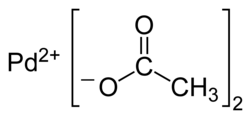
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Palladium (II) acetate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
Pd (OAc) 2 |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | Pd (OCOCH 3 ) 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
Solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 224.51 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
216.3–223.7 ° C (decomposition) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Palladium (II) acetate is a chemical compound of palladium with the semi-structural formula Pd (CH 3 COO) 2 . Palladium (II) acetate dissolves in many organic solvents and is used as a catalyst for organic syntheses. In organometallic chemistry it serves as a precursor for other palladium complexes.
Manufacturing
Palladium (II) acetate can be produced by reacting palladium metal with a mixture of hot nitric acid and acetic acid . Depending on how it is manufactured, palladium (II) acetate can be present as a brown powder with a trimeric structure or as a pink powder with a chain structure.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e data sheet Palladium (II) acetate, ≥99.9% trace metals basis from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on July 16, 2017 ( PDF ).
- ^ TA Stephenson, SM Morehouse, AR Powell, JP Heffer, G. Wilkinson: 667. Carboxylates of palladium, platinum, and rhodium, and their adducts. In: Journal of the Chemical Society . 1965, pp. 3632-3640, doi : 10.1039 / JR9650003632 .
- ↑ Sergei D. Kirik, Ruslan F. Mulagaleev, Alexander I. Blokhin: [Pd (CH 3 COO) 2 ] from X-ray powder diffraction data. In: Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 60, 2004, pp. M449-m450, doi : 10.1107 / S0108270104016129 .
