Pampas
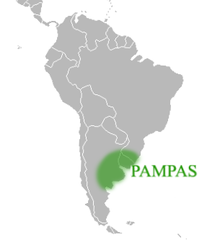
The ecoregion Pampa (often also used in the plural form pampas ) is a subtropical grass steppe in southeastern South America on the Río de la Plata .
The word comes from Quechua and means "level" or "field". Colloquially, the term is transferred to mean "sparsely populated, lonely, remote area".
geography
In the west, the pampas are bounded by the Andes , in the east by the Atlantic . To the north are the dry forests and thorn bush savannahs of the Chaco . The use of the term can be vaguely compared with the Australian Outback , the South African High Veld or the New Zealand High Country .
The states of Argentina , Uruguay and Brazil in particular have a share in the pampas.
It forms the agricultural heartland of Argentina, in which cattle breeding dominates. In the southern pampas the vegetation is becoming increasingly sparse; here the grass is only enough for sheep breeding .
climate
The annual average temperature is around 17 ° C, the annual rainfall averages 800 mm. A distinction is made between the "humid pampas" in the east, which receives regular rainfall throughout the year, and the "dry pampas" in the west, which merge into the shrub steppe of Monte . The mountain ranges of the Sierras Pampeanas lie in this transition area. Typical of the pampas is the extensive occurrence of loess , which has contributed significantly to the fertile soils of the pampas.
The pampas have a temperate climate . In the east the temperature differences between summer and winter are relatively small because of the proximity to the sea, in the west the continental character increases with hot summers and relatively cold, very dry winters.
fauna
Only a sparse number of native animal species can be found in the pampas. However, this is supplemented by species from various adjacent zones ( Chaco , steppe). The inhabitants of the pampas include the guanaco , an ancient species of the llama, and the pampas deer as herbivores. The Viscacha , a rodent species, lives in underground passages and often shares living space with the pampas fox . The mara , the rhea , the owl rabbit and the guinea pig are other pampas inhabitants.
Since the Spanish Conquista in the second third of the 16th century, runaway grazing animals - especially cattle and horses - spread in the pampas, and they quickly multiplied and became wild. They were known as Cimarrones and offered the Indians of the time a new subsistence base as cavalry hunter cultures.
See also
literature
- Samuel Amaral: The Rise of Capitalism on the Pampas - The Estancias of Buenos Aires. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 1998, ISBN 0-521-57248-7 .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Prado, JL, Martinez-Maza, C., & Alberdi, MT (2015). Megafauna extinction in South America: A new chronology for the Argentine Pampas. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 425, 41-49.