Phacidiaceae
| Phacidiaceae | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
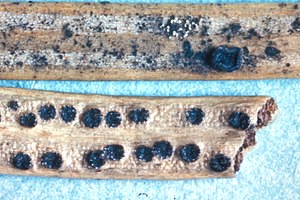
Gremmenia infestans (Syn. Phacidium infestans ) on needles of the Colorado fir |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the order | ||||||||||||
| Phacidiales | ||||||||||||
| Heck. | ||||||||||||
| Scientific name of the family | ||||||||||||
| Phacidiaceae | ||||||||||||
| Fr. |
The Phacidiaceae form the only family of mushrooms within the order of the Phacidiales , which belong to the real sac fungi .
features
Species of the Phacidiaceae family form a black stroma that is embedded in the host tissue. It is rounded and uniloculat, that is, with a single indentation. When fruit bodies are Apothecia formed that grow directly from cells of the central stroma without a separating wall. The apothecia open in radial or longitudinal cracks. The layer between the tubes has a simple structure, which are branched and connected at the base and have paraphyses at the top . As with all Leotiomycetes, the tubes themselves are unitary and thin-walled and cylindrical. They often have an amyloid apical ring (which can be stained with iodine) . The unseptated ascospores are hyaline and without a shell. The secondary crop forms are coelomycetic and stromatically also embedded in the host tissue. The conidiogenic cells are phialidic and cylindrical and develop continuously. The hyaline conidia are cylindrical to oval or slightly kidney-shaped and often with a gelatinous appendage.
ecology
Phacidiaceae are mostly restricted to temperate areas. The species live saprotrophically or parasitically on and in leaves, especially on conifers . Some species are parasites on economically important trees, but they are not significantly damaged.
Systematics
Elias Magnus Fries described the family in 1849 in the Summa vegetabilium Scandinaviae . The family was classified as polyphyletic until recently , but has not been adequately studied. Crous et al. (2014) then carried out an extensive investigation and found that the Phacidiaceae are clearly independent, and re-established the Phacidiales order described by Franz Xaver Rudolf von Höhnel in 1917 , which had previously only been considered a synonym for the Helotiales . They are now a sister clade to the Helotiales. The dirt cup relatives (Bulgariaceae), which had previously also belonged to the Helotiales as an independent family, were recognized as part of the Phacidiaceae and are therefore only a synonym. Both names (Bulgariaceae and Phacidiaceae) were published at the same time, but since the Phacidiaceae includes more species, this name was given preference over Bulgariacae.
The following genera belong to the Phacidiaceae family:
- Allantophomopsiella
- Allantophomopsis
- Bulgaria
- Gremmenia :incorporatedinto Phacidum until 2014
- Phacidium : including the genus Ceuthospora, which was independent until 2014
- Potebniamyces
- Pseudophacidium
swell
literature
- Paul F. Cannon, Paul M. Kirk: Fungal families of the world . CABI Europe, Wallingford, Oxfordshire (UK) 2007, ISBN 978-0-85199-827-5 , pp. 266 ( available online ).
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Pedro W. Crous, William Quaedvlieg, Karen Hansen, David L. Hawksworth, Johannes Z. Groenewald: Phacidium and Ceuthospora (Phacidiaceae) are congeneric: taxonomic and nomenclatural implications. In: IMA Fungus . tape 5 , no. 2 , 2014, p. 173–193 , doi : 10.5598 / imafungus. 2014-05-02-02 ( Phacidium and Ceuthospora (Phacidiaceae) are congeneric: taxonomic and nomenclatural implications. [PDF]).
- ^ Mycobank, accessed April 7, 2015
- ↑ Lumbsch, HT and SM Huhndorf (ed.) 2007: Outline of Ascomycota - 2007. Myconet 13: 1-58. Full text pdf

