Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
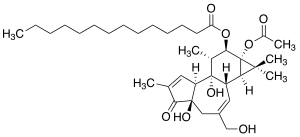
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 36 H 56 O 8 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless powder |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 616.83 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
50-60 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | ||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), alternatively also 12- O -tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate or tetradecanoylphorbol-acetate (TPA), belongs to the group of phorbol esters. The molecule is used in biochemical research to activate protein kinase C (PKC) as a structural analog of diacylglycerol. The effect of PMA results from its structural similarity to one of the natural activators of the PKC isoforms, diacylglycerol .
PMA is a subject of study in the treatment of leukemia . It is particularly useful in cancer diagnostics because it can serve as a B-cell -specific mitogen in a cytogenetic test. In ELISPOT , phorbol esters such as PMA are used as positive controls to demonstrate cell viability and the secretion of cytokines in the cells used.
PMA was first found in a Southeast Asian plant belonging to the Croton genus , which, when touched, causes a rash similar to poison sumac . Plants with higher contents of phorbol esters are problematic feedstuffs in the animal fattening of herbivores.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f data sheet Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, ≥99% (TLC), film or powder from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on October 18, 2012 ( PDF ).
- ↑ M. Castagna, Y. Takai, K. Kaibuchi, K. Sano, U. Kikkawa, Y. Nishizuka: Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters . In: Journal of Biological Chemistry . tape 257 , no. 13 , October 7, 1982, pp. 7847-7851 .
- ↑ Peter M. Blumberg: Protein Kinase C as the Receptor for the Phorbol Ester Tumor Promoters: Sixth Rhoads Memorial Award Lecture . In: Cancer Research . tape 48 , no. 1 , 1988, p. 1-8 .
- ↑ JE Niedel, LJ Kuhn, GR Vandenbark: phorbol diesters receptor copurifies with protein kinase C . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . tape 80 , no. 1 , 1983, p. 36-40 , doi : 10.1073 / pnas.80.1.36 .
- ↑ Margaret J. Barch, T. Knutsen, Jack L. Spurbeck et al. (Ed.): The AGT cytogenetics laboratory manual . 3. Edition. tape 666 . Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphia 1997.
- ^ S. Palzer, T. Bailey, C. Hartnett, A. Grant, M. Tsang, AE Kalyuzhny: Simultaneous detection of multiple cytokines in ELISPOT assays. In: Methods in Molecular Biology (2005), Vol. 302, pp. 273-288. PMID 15937361 .
- ↑ XL Zhang, L. Wang, F. Li, K. Yu, MK Wang: Cytotoxic Phorbol Esters of Croton tiglium. In: J Nat Prod . (2013), Volume 76, Issue 5, pp. 858-864. doi: 10.1021 / np300832n . PMID 23701597 .
- ↑ G. Goel, HP Makkar, G. Francis, K. Becker: Phorbol esters: structure, biological activity, and toxicity in animals. In: Int J Toxicol . (2007), Volume 26, Issue 4, pp. 279-288. PMID 17661218 .
