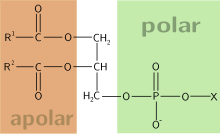
Phosphoglycerides
Phosphoglycerides , also called glycerophospholipids / phosphoglycerolipids , are acylglycerols (glycerides) and belong to the group of phospholipids . They are part of the cell membrane in bacteria and higher organisms and, like all phospholipids, are composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic hydrocarbon residues.
Structure and occurrence
Phosphoglycerides are composed of glycerol , the two fatty acids at two of the hydroxyl groups (OH groups) esterified is. A phosphate group is bound to one of the third, terminal OH groups . This phosphate group is in turn esterified with different alcohols (X). The phosphate group thus forms a phosphoric acid di ester. All naturally occurring phosphoglycerides (with the exception of a few archaea ) have the sn configuration , which defines the stereospecific spatial arrangement of the glycerol substituents.
The structure of phosphoglycerides can also be understood as that of fats in which a fatty acid has been replaced by a phosphoric acid ester. The function and properties of the phosphoglyceride are decisively determined by the two fatty acid residues (R 1 COO- and R 2 COO-) and the alcohol (X). The alcohol can be, for example, serine , choline , inositol or colamine . If it is an esterification with cholines, lecithins (also phosphatidylcholines ) are formed; when esterified with serine, cephalins are formed. If the first fatty acid of a phospholipid is replaced by a long-chain enol ether or an aldehyde with 16–20 carbon atoms, the resulting phosphoglycerides are called plasmalogens .
The occurrence of phosphoglycerides is particularly high in the spinal cord (6–10%, based on the total fat content), brain (3.7–6%), liver (1–5%), heart (1–3%) and in the egg yolk ( 8-10%). Phosphorus glycerides are also found in plants, in seeds and roots.
| class | Structural formula | Remainder X |
|---|---|---|
| Phosphatidic acid |

|
Hydrogen atom |
| Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) |

|
Choline |
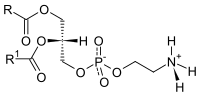
| Phosphatidylethanolamine |
|
Ethanolamine |
| Phosphatidylinositol |

|
Inositol |
| Phosphatidylserine |

|
Serine |
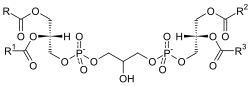
| Diphosphatidyl glycerin (cardiolipin) |
|
Glycerol phosphatidic acid |
biosynthesis
In bacteria, phosphatidylethanolamine is produced from phosphatidylserine by decarboxylation , mediated by phosphatidylserine decarboxylases ( Psd ). Cardiolipin is produced in bacteria by one of several cardiolipin ligases ( CL ).
Meaning and use
Phosphatidylinositol is part of some signal transmission pathways within the body, for example those of some hormones, and also serves to anchor proteins in the cell membrane.
Phosphatidylserine is externalized as an "eat me" signal during apoptosis of cells.
Ammonium salts of phosphatidic acids are used under the designation E 442 ( ammonium phosphatide ) as food additives ( emulsifiers and stabilizers ) in cocoa and chocolate products.
literature
- PP Ho, JL Kanter u. a .: Identification of Naturally Occurring Fatty Acids of the Myelin Sheath That Resolve Neuroinflammation. In: Science Translational Medicine . 4, 2012, pp. 137ra73-137ra73, doi: 10.1126 / scitranslmed.3003831 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Gregory Cevc: Phospholipids Handbook. CRC Press, 1993, ISBN 978-0-8247-9050-9 , p. 2.
- ^ R. Moser, M. Aktas, C. Fritz, F. Narberhaus: Discovery of a bifunctional cardiolipin / phosphatidylethanolamine synthase in bacteria. In: Molecular microbiology. Volume 92, Number 5, June 2014, pp. 959-972, doi: 10.1111 / mmi.12603 . PMID 24707916 .