Phosphol
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
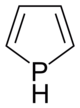
|
||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Surname | Phosphol | |||||||||
| other names |
1 H -phosphole |
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 5 P | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 84.06 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
Phosphol is an organic compound with the empirical formula C 4 H 5 P; it is the phosphorus- analogous variant of pyrrole .
history
A phosphole derivative was first discovered in 1953, pentaphenylphosphole followed in 1959. The synthesis of the title compound was described in 1987.
presentation
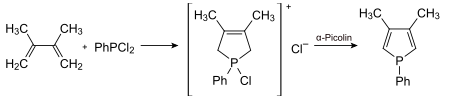
In general, phospholes are prepared from butadienes and dichlorophosphanes using the McCormack reaction .
In the example shown, the phenyl ring can then be cleaved with butyllithium .
properties
In contrast to other five-membered heterocycles such as pyrrole , thiophene and furan , phosphole has no aromaticity , since phosphorus does not make its lone pair of electrons available to the π-electron pairs within the ring for the purpose of delocalization .
The phospholide anions obtained with the representation explained in the above section dimerize on protonation . This dimerization can be reversed by heating and the thermodynamically more stable exo dimer is obtained in analogy to cyclopentadienes .
Because of the dimerization, the phosphole can only be characterized at low temperatures by means of 31 P { 1 H} NMR . The chemical shift for the anion is + 76.6ppm, for the phosphole it is −49.2ppm with a 1 J PH coupling constant of 234 Hz in THF.
Further physical data such as boiling point, melting point etc. or toxicological properties are therefore not known.
Transition metal complexes
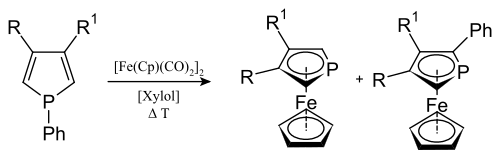
Analogously to other metallocenes , phosphaferrocenes can be produced from phospholes .
Many other transition metal complexes are known from the phospholyl ligand (phosphacyclopentadienyl) and its derivatives. The ligands (L) appear as 2, 3, 4, 5 or in anionic form as 6-electron donors, with complete localization of the ring π-electrons in terminal complexes such as LM (CO) n for example [(CO) 5 W (PC 4 H 2 Me 2 ) {η 5 -W (CO) 5 }] via metal-bridged 3-electron ligands (µ-L) M 2 (CO) 8 for example (µ-PC 4 H 2 Me 2 ) Mn 2 (CO) 8 up to complete delocalization as η 5 ligand in η 5 - (Me 2 C 4 H 2 P) W (CO) 3 I or in phosphaferrocene.
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ^ PJ Fagan, WA Nugent: 1-Phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetramethylphosphole In: Organic Syntheses . 70, 1992, p. 272, doi : 10.15227 / orgsyn.070.0272 ; Coll. Vol. 9, 1998, p. 653 ( PDF ).
- ^ WB McCormack: US Pat. 2,663,736 and 2,663,737. Full text ( memento of the original from September 24, 2007 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ C. Charrier, H. Bonnard, G. de Lauzon, F. Mathey: Proton [1,5] shifts in P-unsubstituted 1H-phospholes. Synthesis and chemistry of 2H-phosphole dimers , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1983 , 105 , 6871-6877; doi: 10.1021 / ja00361a022 .
- ↑ F. Mathey, A. Mitschler, R. Weiss: Phosphaferrocene , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1977 , 99 , 3537-3538; doi: 10.1021 / ja00452a076 .
- ↑ EW Abel, N. Clark, C. Towers: η-Tetraphenylphospholyl and η-tetraphenylarsolyl derivatives of manganese, rhenium, and iron , in: J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. , 1979 , 1552-1556; doi: 10.1039 / DT9790001552 .
- ^ S. Holand, F. Mathey, J. Fischer, A. Mitschler: Preparation of 3,3 ', 4,4'-tetramethyl-1,1'-biphospholyl and its reactions with iron and cobalt carbonyls , in: Organomet. , 1983 , 2 , 1234-1238; doi: 10.1021 / om50003a027 .
- ^ S. Holand, C. Charrier, F. Mathey, J. Fischer, A. Mitschler: Stabilization of 2H-phospholes by complexation. A phosphorus-carbon double bond acting as a four-electron donor , in: J. Am. Chem. Soc. , 1984 , 106 , 826-828; doi: 10.1021 / ja00315a081 .
- ↑ U. Flörke, O. Krampe, H.-J. Main: bis (µ-3,4-dimethylphosphol-1-yl) bis (tetracarbonylmanganese) , in: Act. Cryst. C , 1998 , 54 , 918-920; doi: 10.1107 / S0108270198001036 .
- ↑ S. Holand, F. Mathey, J. Fischer: Synthesis and x-ray crystal structure analysis of (η 5 -3-4-dimethylphospholyl) tricarbonyl-iodotungsten , in: Polyhedron , 1986 , 5 , 1413-1421; doi: 10.1016 / S0277-5387 (00) 83502-0 .
further reading
- Louis D. Quin: A Guide to Organophosphorus Chemistry . John Wiley & Sons, 2000, ISBN 0-471-31824-8 .