Pioneer 3
| Pioneer 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
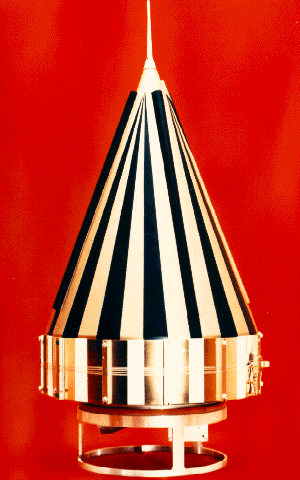 Image of the Pioneer 3 probe |
|||||||
| NSSDC ID | 1958-008A | ||||||
| Mission goal | Images of the lunar surface | ||||||
| Client |
|
||||||
| Launcher | Juno II (5-stage) | ||||||
| Course of the mission | |||||||
| Start date | December 6, 1958, 05:45 UTC | ||||||
| launch pad | CCAFS , LC-5 | ||||||
| End date | 7th December 1958 | ||||||
|
|||||||
Pioneer 3 was a space probe from the US space agency NASA as part of the Pioneer program. It was supposed to take pictures of the moon, but it did not reach the required speed and burned up when it reentered the earth's atmosphere.
construction
Pioneer 3 consisted of a conical fiberglass structure 58 cm high and 25 cm in diameter, the tip of which was designed as an antenna. The outside was gold-plated to make it electrically conductive and provided with white stripes for thermal control. The probe was powered by mercury batteries and carried a transmitter with a power of 0.18 W at 960.05 MHz. To reduce the spin rate from 400 / min to 6 / min, two disposable masses of 7 g each ("yo-yo masses") were attached to the outside.
mission
Pioneer 3 was much smaller and lighter than its three predecessor probes Pioneer 0 , Pioneer 1 and Pioneer 2 and was launched on December 6, 1958 at 05:45 UTC by means of a relatively poorly powered Juno II launcher. The probe should pass the moon and then go into heliocentric orbit. It only reached a summit height of 102,360 km before falling back to earth because the burnout occurred 3.7 seconds too early. The correct entry angle was also missed. As an alternative program, the Van Allen radiation belt was measured using two Geiger-Müller counter tubes and the triggering of the moon camera was tested. After a flight time of a good 38 hours, the probe burned up in the earth's atmosphere.
Web links
- Pioneer 3 in the NSSDCA Master Catalog (English)
