Plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition
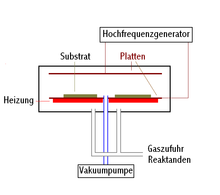
The plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition ( English plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition , PECVD;. And English plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition , PACVD called) is a special form of chemical vapor deposition (CVD), in which the deposition by a plasma is supported. The plasma can burn directly next to the substrate to be coated (direct plasma method) or in a separate chamber (remote plasma method).
functionality

While in CVD the dissociation (breaking up) of the molecules of the reaction gas takes place through the external supply of heat and the energy released by the following chemical reactions, this task is performed in PECVD by accelerated electrons in the plasma. In addition to the radicals formed in this way, ions are also generated in a plasma which, together with the radicals, cause the layer to be deposited on the substrate. The gas temperature in the plasma usually only increases by a few hundred degrees Celsius, which means that, in contrast to CVD, more temperature-sensitive materials can also be coated.
In the direct plasma method , a strong electric field is applied between the substrate to be coated and a counter electrode, which ignites a plasma. With the remote plasma method , the plasma is arranged in such a way that it has no direct contact with the substrate. This achieves advantages with regard to selective excitation of individual components of a process gas mixture and reduces the possibility of plasma damage to the substrate surface by the ions. Disadvantages may be the loss of radicals on the route between remote plasma and substrate and the possibility of gas phase reactions before the reactive gas molecules have reached the substrate surface.
The plasmas can also be generated inductively / capacitively by irradiating an electromagnetic alternating field, whereby electrodes are superfluous.
Examples
With PECVD, amorphous silicon , silicon nitride , silicon dioxide and silicon-oxide-nitride compounds and much more can be deposited (e.g. carbon nanotubes ).
Layers made of the semiconductor material silicon are made from monosilane or silicon tetrachloride :
Dielectric layers made of silicon dioxide can be made of monosilane and e.g. B. Nitric oxide can be produced:
Layers of silicon nitride used for passivation can be produced from monosilane and nitrogen :
Layers of aluminum , which has the function of an electrical conductor in switching elements , can be produced from aluminum chloride and hydrogen:
See also
literature
- Eugen Unger: The production of thin layers. The PECVD process: vapor deposition in a plasma . In: Chemistry in Our Time . tape 25 , no. 3 , 1991, pp. 148–158 , doi : 10.1002 / ciuz.19910250306 .