Pleomorphic adenoma
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| D11.0 | Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The pleomorphic adenoma is a benign tumor that often in the parotid gland , occurs (parotid) rare in other salivary glands. With a share of 85%, it is the most common benign neoplasm of the salivary glands and makes up about half of all salivary gland tumors in total.
Pleomorphic adenomas grow slowly and remain asymptomatic for a long time. The therapy of choice is the surgical removal of the tumor, with which a definitive healing can be achieved. If, however, remnants of the tumor remain in the body, persistent recurrences can result. In addition, a malignant tumor can develop within a pleomorphic adenoma, whereby the risk is initially low and only increases over time.
Epidemiology
The age peak is in the 4th – 6th Decade of life, the mean age of onset is 43 years. Women are affected slightly more often than men (3: 2). White people are more likely to get the disease than people of other colors.
etiology
The underlying causes of tumor development are unknown. In contrast to the Warthin tumor , the second most common tumor of the parotid gland, there is apparently no association with cigarette smoking.
A translocation and overexpression of the genes PLAG ( chromosome 8q) and HMGA2 (chromosome 12q) that code for transcription factors are of molecular genetic importance for the development of pleomorphic adenomas .
pathology
The main localization of the pleomorphic adenoma is the parotid gland (85%), followed by the small salivary glands (10%) and the mandibular salivary gland (5%). Less common places of manifestation are the sublingual salivary gland , lacrimal gland , the tracheobronchial system , the nasal cavity , skin , mammary gland or the soft tissue . Within the parotid gland, the tumor usually affects the superficial (75%), less often the deep (25%) glandular lobes.
Macroscopically, the tumor appears as a few millimeters to several centimeters in size, well-circumscribed, rubbery-elastic or fleshy, gray-white tissue with a mucoid or shiny cut surface. Recurring tumors are often multi- nodular.
Histologically , there is a tumor, often delimited by a thin connective tissue capsule, with a varied histoarchitecture made up of epithelial and modified myoepithelial cells. These form strand-like, duct-like and solid associations or are distributed like swarms of bees within an alternately extensive mucoid, myxoid or chondroid stroma .
Immunohistochemistry
The epithelial component of the tumor shows a positivity for carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), the epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), c-kit and, to varying degrees, also for S-100. Reliable markers of the myoepithelial component are p63 and calponin in particular ; there is also positivity for cytokeratins , S-100 or GFAP .
The expression of the markers Ki-67 and p53 is helpful in the differential diagnosis of adenoid-cystic carcinoma . While these are expressed in an average of 1.6 and 1.2 percent of tumor cells in pleomorphic adenomas, 20–55 and 4–24 percent of tumor cells are positive in adenoid-cystic carcinoma. In addition, adenoid-cystic carcinomas show a much stronger expression of the marker bcl-2 .
diagnosis
Pleomorphic adenomas are usually clinically noticeable as a slowly growing, solid resistance. Incidentally, the tumors are largely symptom-free and are not infrequently discovered by chance during routine examinations. Often times, the lesions have been in place for a year or more before the patient see the doctor.
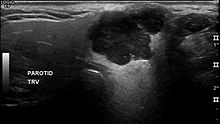
The extent of the finding can be determined by means of imaging methods ( magnetic resonance tomography , computed tomography or sonography ). A definitive diagnosis is made by the pathologist through a histological examination of the surgical specimen or sometimes using cell material obtained during a preoperative fine needle aspiration .
Differential diagnosis
Clinical differential diagnoses are Warthin's tumor and other salivary gland tumors, sarcoid , lymphoma, or lymphadenopathy .
Tumors to be excluded in the context of histological diagnosis are, in particular, monomorphic adenomas ( basal cell adenoma , myoepithelioma ), adenoid-cystic carcinoma , polymorphic low-grade adenocarcinoma , mucoepidermoid carcinoma and various mesenchymal neoplasms.
therapy
The treatment of choice is complete surgical removal of the finding. If the parotid gland is affected, this usually means a partial removal (partial parotidectomy ) of the gland while protecting the facial nerve , but with a safety margin in healthy tissue. Radical parotidectomy with removal of the nerve is rarely indicated. The mere peeling of the tumor tissue in the sense of enucleation is no longer considered sufficient today due to the high tendency to recur and the risk of the tumor tissue being spread.
forecast
With the usual surgical procedure, recurrence rates of 1 to 5 percent have been described. If the findings are only peeled off (enucleation), a recurrence of the tumor can be observed in up to 50 percent of the cases. Stromal tumors are evidently more prone to recurrence, presumably because the surgery tends to spread the often soft stroma. On the other hand, cell-rich tumors are possibly associated with an increased risk of degeneration. According to various studies, the risk of developing a malignant tumor in a pleomorphic adenoma ( carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma ) is given as 2–23 percent, with an average of 6 percent, the longer the diagnosis, the higher the frequency of degeneration.
A metastasis of actually benign tumor is observed. Since these are often only observed after many years of multiple operations and the metastases, like the primary tumor, often do not reveal any malignancy criteria , it is assumed that the spread of tumor tissue during the operation, for example via opened vessels, could play a role. Tumor settlements are found in decreasing frequency in the bones (50 percent), lungs (30 percent) and lymph nodes (30 percent) and rarely in other locations such as the scalp , abdominal wall or liver .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f A. L. Wagner, J. Haag: Parotid, Pleomorphic Adenoma. (April 18, 2007); http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/384327-overview
- ↑ a b U. Riede, M. Werner, H. Schäfer: General and special pathology. 5th edition. Thieme, 2004, ISBN 3-13-683305-8 .
- ↑ a b c d e f C. DM Fletcher: Histopathology of Tumors. 3. Edition. Churchill Livingston Elsevier, 2007, ISBN 978-0-443-07434-9 .
- ↑ S. Sadetzki, B. Oberman, L. Mandelzweig, A. Chetrit, T. Ben-Tal, A. Jarus-Hakak, S. Duvdevani, E. Cardis, M. Wolf: Smoking and risk of parotid gland tumors: a nationwide case-control study . IN: Cancer . 2008 May 1; 112 (9), pp. 1974-1982. PMID 18361448 .
- ↑ ML Voz, WJ Van de Ven, K. Kas: First insights into the molecular basis of pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary glands . Adv Dent Res. 2000 Dec; 14, pp. 81-83. PMID 11842929 .
- ^ AF Marshall, DR White, WW Shockley: Pleomorphic adenoma in the palpebral lobe of the lacrimal gland. In: Arch Pathol Lab Med . 2004 Dec; 128 (12), pp. 1385-1394. PMID 15578883
- ↑ HA Gaissert, EJ Mark: Tracheobronchial gland tumors. In: Cancer Control . 2006 Oct; 13 (4), pp. 286-294. PMID 17075566
- ↑ MF Karakus, KM Ozcan, H. Dere: Endoscopic resection of pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. In: Tumori. 2007 May-Jun; 93 (3), pp. 300-301. PMID 17679469
- ↑ K. Sato, Y. Ueda, M. Shimasaki, M. Ozaki, N. Nitta, K. Chada, Y. Ishikawa, S. Katsuda: Pleomorphic adenoma (benign mixed tumor) of the breast: a case report and review of the literature. In: Pathol Res Pract. 2005; 201 (4), pp. 333-339. PMID 15991841 .
- ↑ PathConsult: Benign Mixed Tumor (6 January 2006), Elsevier; http://www.pathconsultddx.com/pathCon/diagnosis?TXTBOX2=pleo&pii=S1559-8675%2806%2970117-6 ( page no longer available , search in web archives ) Info: The link was automatically marked as defective. Please check the link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.