Quaternization

In chemistry, quaternization describes the conversion of suitable atoms into the quaternary degree of substitution with four organic radicals . The quaternization is thus a subgroup of the alkylations , through which a certain product class is created. Here the central atom receives four identical or different organic substituents and a positive charge - a cation is thus formed. Haloalkanes or dimethyl sulfate are used as alkylating agents ; the counterion (anion) is then a halide , e.g. B. chloride , bromide , iodide , or sulfate or methyl sulfate .
Examples
Conversion of amines to quaternary ammonium compounds
The quaternization of tertiary amines to quaternary ammonium compounds is shown using the alkylation of a tertiary amine (R = organyl group, e.g. alkyl group):
| Quaternization of amines | Quaternization with spatially drawn p orbital |
|---|---|

|

|
If you start from a primary amine (= alkylamine) and this is reacted in stages with excess haloalkane , the intermediate products are obtained
- secondary amine (= dialkylamine ) and
- tertiary amine (= trialkylamine )
analogous to a quaternary ammonium halide. The reaction of trimethylamine with iodomethane produces tetramethylammonium iodide:
Similarly, when trimethylamine is reacted with bromomethane, tetramethylammonium bromide is formed:
The simplest quaternary ammonium compound is tetramethylammonium chloride .
Conversion of pyridine to pyridinium compounds
An example of a quaternization is the reaction of pyridine to a pyridinium compound (R = organyl group, e.g. alkyl group):
| Quaternization of pyridine | Quaternization with spatially drawn p orbital |
|---|---|
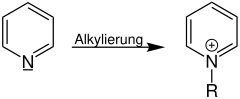
|

|
Conversion of phosphines to phosphonium salts
The reaction of a phosphine to a quaternary phosphonium compound is also called quaternization (R = organyl group, e.g. alkyl group):
| Quaternization of Phosphanes | Quaternization with spatially drawn p orbital |
|---|---|

|

|
As an alkylating agent, a haloalkane - z. B. Bromomethane - are used; this gives a phosphonium bromide.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Jürgen Falbe , Manfred Regitz : Römpp-Chemie-Lexikon . 9th edition. Thieme, Stuttgart 1992, ISBN 3-13-735009-3 , p. 3736 .
- ↑ Joachim Buddrus, Bernd Schmidt: Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry , 5th Edition, de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin 2015, ISBN 978-3-11-030559-3 , p. 675.
- ↑ Joachim Buddrus, Bernd Schmidt: Basics of Organic Chemistry , 5th edition, de Gruyter Verlag, Berlin 2015, ISBN 978-3-11-030559-3 , p. 493.

