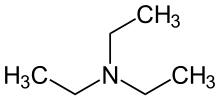
Trialkylamines

Trialkylamines form a group of organic chemical compounds that are derived from ammonia (NH 3 ), the three hydrogen atoms of which have been replaced by alkyl radicals R. If the three radicals R are the same, the trialkylamines have the general formula NR 3 . The best known trialkylamine is triethylamine [N (C 2 H 5 ) 3 ].
The three alkyl radicals in the trialkylamines can also be completely or partially different. Such trialkylamines are less important than the representatives with three identical alkyl groups. However, diisopropylethylamine (Hünig base) is known.
Manufacturing
The reaction of ammonia with three equivalents of a reactive haloalkane , e.g. B. iodoethane , provides the corresponding trialkylamines, e.g. B. triethylamine. In a technical process for the production of triethylamine, ammonia and ethanol are the starting materials.
use
Trialkylamines, particularly often triethylamine, are used as a basic solvent in synthetic organic chemistry . Trialkylamines are also often used as an auxiliary base in order to bind acids released during reactions (cf. also: diisopropylethylamine ). An example is the formation of esters from carboxylic acid chlorides and alcohols , in which hydrochloric acid is released. The acid is bound by the formation of trialkylammonium salts, in the case of hydrochloric acid that is, trialkylammonium chloride (see also: Hydrochloride ). Triethylamines are also used as catalysts in the production of various plastics and synthetic resins , such as polyurethanes and phenoplasts .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Ed.): Römpps Chemie-Lexikon. Volume 6: T-Z. 8th revised and expanded edition. Franckh'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart 1988, ISBN 3-440-04516-1 , p. 4334.