Phenoplast
Phenoplasts ( DIN - Abbreviation : PF) are thermosetting plastics that are produced on the basis of phenolic resins by curing. Phenolic resins (PF resins, phenol-formaldehyde resins) are synthetic resins ( condensation resins) that are produced from phenols and aldehydes by polycondensation . Important starting materials for the production of the resins are phenol and formaldehyde .
history
Phenoplasts are among the first industrially produced plastics. The first phenoplast to be produced on a large scale is phenol-formaldehyde condensation resin, invented by Leo Hendrik Baekeland in 1907 , which was marketed under the Bakelite trademark and used in many areas for decades. Because of their temperature resistance, surface hardness and the low price, phenoplasts are still the most important thermosets today and are used, among other things, to manufacture brake linings .
Manufacturing
Phenoplasts consist of hardened phenolic resins that are obtained by synthesizing phenols with aldehydes . In addition to phenol, compounds such as 3-cresol , 3,5-xylenol or resorcinol are also used.
By electrophilic substitution of phenol, acid - catalyzed precursors are formed which, depending on the amount of formaldehyde used, carry one to three hydroxymethyl groups (–CH 2 –OH). The acidic catalysts used include hydrochloric acid or oxalic acid . The substitution takes place only in the ortho or para position of the phenol:
It forms o -Hydroxymethylphenol (1) and p -Hydroxymethylphenol (2). With an excess of formaldehyde and under basic conditions, compounds with up to three hydroxymethyl groups can form. The resins are formed by catalyzed polycondensation of these phenol derivatives . Depending on the desired result, the precondensates are then mixed with acidic or basic condensation agents .
Novolaks : In an acidic environment, oligomers , the so-called novolaks, are formed from the phenyl alcohols through condensation via a methylene group (–CH 2 -) . Formaldehyde and phenols are converted in a ratio of 4: 5 or less formaldehyde:
Novolaks are semi-liquid or still meltable. They are stable in storage, i.e. not self-curing. Together with formaldehyde donors such as hexamethylenetetramine, novolaks harden at temperatures above 120 ° C to form infusible, thermosetting compounds.
Resoles : With basic condensation agents , on the other hand, meltable resins, which are soluble in many solvents, are formed , the resoles . The larger amounts of formaldehyde usually used (up to 2.5: 1) result in not only methylene groups but also ether groups being formed.
Resoles tend to self-harden through further condensation and form the intermediate stage resitol . If the precondensates are heated, crosslinked polymers, the infusible and insoluble final stage, the resist , are obtained with further elimination of water .
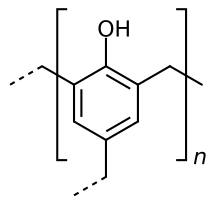
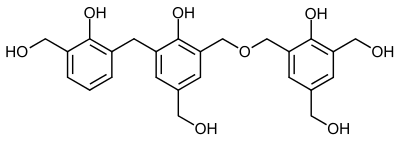
After the resin has cured, closely-meshed crosslinked polymers are formed, since the phenol groups are linked to one another by up to three methylene groups.

Possible structure of a phenoplast. Dashed lines indicate the continuation of the macromolecule .
properties
- Density: 1.30… 1.45 g / cm³
- hard, very break-proof
- yellow to brown; darkens when exposed to light
- only machining possible
- Firing test : mostly flame retardant; yellowish flame; easily sprays sparks; Material cracks and cracks and becomes charred; Phenol and formaldehyde smell
use

- Resin molded parts
- Fillers such as wood flour , soot , graphite , quartz sand , glass dust or textile fibers give the phenoplasts more substance and greater strength. Together with the additives, the resins form molding compounds and are used in the molding process to produce stable, heat-resistant and relatively heavy plastic parts. Injection molding processes are also possible with small amounts of additives . Compression molded products such as handles and housing parts of heat-stressed household and electrical appliances , billiard balls and cone balls are manufactured with fillers .
- Laminates
- To produce fiber composite materials , strips of wood, paper or fabric are laid one on top of the other in several strips, impregnated with low-viscosity phenolic resin and pressed. The material hardens at temperatures above 150 ° C. The resulting products are, for example, hard paper and printed circuit boards made from it , hard fabric for machine parts and insulating materials , synthetic resin press wood (impregnated wood). Phenolic resin fiber composites with carbon fibers serve as heat shields with high temperature resistance for aircraft and rocket construction. Car body parts, for example the Trabant , also consisted of this fiber composite (phenoplast and cotton fibers).
Pure phenolic resins are used, among other things, for the production of paints, adhesives, fillers and foams.
Environmental relevance
While the cured products are largely free of pollutant emissions, when heated (processing, fire, failure of insulating materials), phenol and formaldehyde, among other things, are released, i.e. the two toxic starting materials.
Also known is the gradual outgassing of formaldehyde from chipboard , plywood , OSB panels and MDF panels in furniture and interior fittings due to the adhesive that is not completely chemically set. Phenolic resin adhesives are sometimes used here. The resin content is up to about 12%. For this reason, these substances are also problematic in domestic fires . Burning in your own stove or in the garden is considered to be unauthorized handling of waste (Criminal Code Section 326).
Trade names
Aramith , Bakelit , Erinoplast , Catalin , Kerit, Pertinax , Plastacart, Plastaflex, Prestofol, Resitex , Sprelacart , GESADUR, Linax, Novotex , Resinol, Supraplast, Ruwatex, Prefere, Vyncolit, Phenodur, Uravar
Norms
- EN 13166 Thermal insulation products for buildings - Factory made phenolic foam (PF) products - Specification .
Derivatives
A copolymer of phenol, formaldehyde and urea , which is then sulfonylated , is used medicinally as a topical tanning agent at Intertrigo under the trade name Tannolact .
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ A b Wolfgang Kaiser : Synthetic chemistry for engineers. From synthesis to application. 3. Edition. Carl Hanser, Munich 2011, ISBN 978-3-446-43047-1 , p. 411 ff.
- ↑ Manfred D. Lechner, Klaus Gehrke, Eckhard H. Nordmeier (eds.): Makromolekulare Chemie. A textbook for chemists, physicists, materials scientists and process engineers. 4th, revised and expanded edition. Birkhäuser, Basel et al. 2010, ISBN 978-3-7643-8890-4 , pp. 130-132.
- ↑ Hans-Dieter Jakubke, Ruth Karcher (Ed.): Lexikon der Chemie. A to Z. Spectrum - Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg et al. 2001, ISBN 3-8274-1152-1 .
- ^ Karlheinz Biederbick: Plastics. 4th, revised and expanded edition. Vogel, Würzburg 1977, ISBN 3-8023-0010-6 , p. 136.
- ↑ [1] Information from the engineering and expert office Wolfgang Gabler on smoke from various plastic materials, accessed on June 8, 2020
- ^ Gerhard Holzmann, Matthias Wangelin, Rainer Bruns: Natural and vegetable building materials , Springer-Verlag 2012, 394 pages, page 32