Red River Colony
The Red River Colony , English Red River Colony , Red River Settlement or Selkirk Settlement , was originally a settlement project of the Scottish Earl Lord Selkirk and the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), which was initiated in Canada in 1812 . Until the founding of the Canadian province of Manitoba in 1870, the settlement area around today's Winnipeg was called that, sometimes also as the Red River District or The Red River .
In 1812, the HBC left a 300,000 km² area to Selkirk from the Ruperts Land administered by it as part of its fur trade monopoly . Selkirk wanted to settle Scottish smallholders there who had become landless in their homeland ( Highland Clearances ). In addition to shorter supply routes to their hunting grounds, the HBC hoped to weaken its largest competitor, the North West Company (NWC). The NWC was based in Montréal and in order to reach the hunting areas of their fur trade monopoly, which are mainly located in the Canadian Rockies , they had to cross the area that was now given to Lord Selkirk. In addition, the Métis who supplied the NWC with the food pemmican, which is essential for the fur trade, also settled there .
The vast territory stretching far beyond the current provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan and Alberta , and the northern edge of the Midwest of the United States , but should be settled first only a small area around the confluence of the Assiniboine and Red River , the Forks called, and probably It is no coincidence that it is also the center of the Métis settlements and the location of Fort Gibraltar , an important trading post of the NWC. The arrival of the first settlers therefore triggered the pemmican war between HBC and NWC. After its end and the merger of the weakened competitors HBC and NWC in 1821, only a few Scots settled there. Under Red River Colony or the Red River one understood from then on the area around the Forks , which was still mainly inhabited by Métis. The combined fur traders renamed Fort Gibraltar in 1822 Fort Garry, from which the settlement area and other parts of the original Red River colony were administered as Assiniboia .
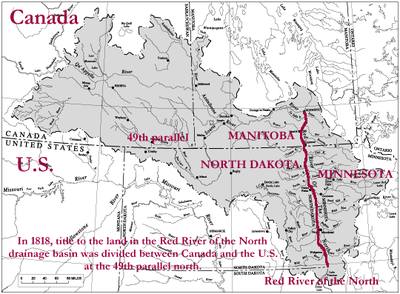
Already in 1818 the south of the 49th northern was latitude location of the Red River Colony territory of the United States , now North Dakota , Minnesota , South Dakota and Montana belong. For the settlement area at The Forks , however, that had no meaning.
In 1869 the HBC sold all of Rupert's land to the Canadian Dominion , which had been founded two years earlier, and in 1870 the area around The Forks became the new province of Manitoba as a result of the Red River Rebellion (see Manitoba Act ). The capital of Manitoba was initially Fort Garry, which in 1873 was combined with the rapidly developing surrounding settlements to form the new city of Winnipeg. By 1912, the Manitoba area had expanded well beyond its initial size to its present size as far as Hudson Bay .
See also
literature
- Alexander Ross: The Red River Settlement , Smith, Elder & Co, London 1856 (on Google Books )
- George Carter: Lord Selkirk and Red River Colony. In: Montana: The Magazine of Western History , Helena (Montana) 1968, Montana Historical Society, 18 (1), pp. 60-69
- Gerard Ens: Prologue to the Red River Resistance: Pre-liminal Politics and the Triumph of Riel. In: Journal of the Canadian Historical Association , Ottawa 1994, Canadian Historical Association, 5 (1), pp. 111–123 ( online )
- The Romantic Settlement of Lord Selkirk's Colonists , by George Bryce , on Project Gutenberg ( online )
- KG Davies: From Competition to Union. In: Minnesota History , St. Paul (Virginia) 1966, Minnesota Historical Society Press, 23 (1), pp. 166-177
- MS Donnelly: Parliamentary Government in Manitoba. In: The Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science , Montreal 1957, Canadian Economics Association, 23 (1), pp. 20–32 ( online )
Web links
- Red River Colony on The Canadian Encyclopedia
- Memorable Manitobans: Governors of the Red River Settlement on the Manitoba Historical Society website
Coordinates: 49 ° 0 ′ 0 ″ N , 97 ° 14 ′ 15 ″ W.