Rudolf Halin
Rudolf Halin (born February 3, 1934 in Uerdingen ; † November 7, 2014 in Mölln ) was a German mathematician who dealt with graph theory and especially with infinite graphs.
Halin received his doctorate in 1962 at the University of Cologne under Klaus Wagner ( "About a graph-theoretical basic term and its application to color problems" ). In 1966 he qualified as a professor in Cologne and in 1971 he became department director and professor at the University of Hamburg . In 1971/72 he was visiting professor at Western Michigan University and in 1977 at Aarhus University.
In 1964 he defined ends in infinite graphs as equivalence classes infinitely long paths ( subgraph in which a node the degree has 1, and the rest level 2, two ways are equivalent if a third exists an infinite number of nodes of the two contains). In 1965 he proved his grid theorem ( Halin's grid theorem ), which says that infinite plane graphs with thick ends (i.e. ends with an infinite number of pairwise disjoint paths) are exactly those that contain sublattices of the plane hexagonal lattice .
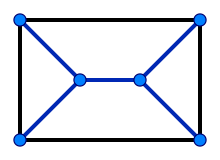
Halin graphs, which he studied in 1971, are named after him. They are flat and arise from trees with at least four nodes, none of which are degree 2, by connecting the leaves of the tree through a cycle . The graphs are significant because many algorithmic problems can be efficiently solved on them, but not on general planar graphs .
In 1974 he expanded Menger's theorem to include infinite graphs.
In 1976 he introduced the terms tree cutting and tree width (under a different name) . The term was introduced under a different name in 1972 by Umberto Bertelé and Francesco Brioschi and again independently of Neil Robertson and Paul Seymour in 1984 in their work on the minor theorem .
In 2000 he published a list of open problems about infinite graphs.
Fonts
- Graph Theory , 2 volumes, research results, Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft 1980, 1981, 2nd edition in one volume 1989
- About infinite paths in graphs , Mathematische Annalen, Volume 157, 1964, pp. 125-137
- About the maximum number of alien infinite paths in graphs , Mathematische Nachrichten, Volume 30, 1965, pp. 63–85
- Studies on minimally n-connected graphs , Combinatorial Mathematics and its Applications (Proc. Conf., Oxford, 1969), London: Academic Press, 1971, pp. 129-136 (Halin Graphen)
- A note on Menger's theorem for infinite locally finite graphs , treatises from the Mathematical Seminar of the University of Hamburg, Volume 40, 1974, pp. 111-114
- S-functions for graphs , Journal of Geometry, Volume 8, 1976, pp. 171-186
- Miscellaneous problems on infinite graphs , Journal of Graph Theory, Volume 35, 2000, pp. 128-151
Individual evidence
- ↑ Kürschner's Scholars Calendar 2009
- ↑ Reinhard thistle in Dmanet
- ^ Rudolf Halin in the Mathematics Genealogy Project (English)
- ^ Weisstein, Halin graphs , Mathworld
- ^ RG Parker, Halin graph , Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer
- ↑ Halin, S-functions for graphs, J. Geom., 8, 1976, 171-186
- ↑ Reinhard Diestel, Graphentheorie, Springer 2012, p. 308
- ↑ Bertelé, Brioschi, Nonserial Dynamic Programming, Academic Press 1972, there called Dimension
- ^ Robertson, Seymour: Graph minors III: Planar tree-width, Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, Volume 36, 1984, pp. 49-64
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Halin, Rudolf |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German mathematician |
| DATE OF BIRTH | February 3, 1934 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Uerdingen |
| DATE OF DEATH | November 7, 2014 |
| Place of death | Mölln |