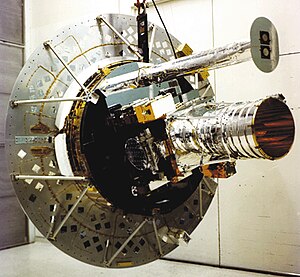
Solar Mesosphere Explorer
| Solar Mesosphere Explorer | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Type: | Research satellite |
| Country: |
|
| Operator: | NASA |
| COSPAR-ID : | 1981-100A |
| Mission dates | |
| Dimensions: | 145 kg |
| Size: | 1.7 m high, 1.25 m diameter |
| Begin: | October 6, 1981, 11:27 UTC |
| Starting place: | Vandenberg Air Force Base SLC-2W |
| Launcher: | Delta-2310 D-157 |
| Flight duration: | 7.5 years |
| Status: | out of service since April 4, 1989, burned up on March 5, 1991 |
| Orbit data | |
| Rotation time : | 91.3 min |
| Orbit inclination : | 97.6 ° |
| Apogee height : | 337 km |
| Perigee height : | 335 km |
The Solar Mesosphere Explorer ( SME ) or Explorer 64 was a research satellite of NASA , the ozone-generating and -zerstörenden processes in the mesosphere and upper stratosphere has researched the earth and the influence of solar radiation on these processes. The satellite was launched from Vandenberg on October 6, 1981 with a Delta 2310 rocket. After launch, SME entered a sun-synchronous low earth orbit. It was spin stabilized at 5 revolutions per minute.
SME was 1.7 m high, 1.25 m in diameter and consisted of two main modules, the satellite bus and the instrument panel. For the scientific measurements, SME had five instruments.
SME transmitted data to Earth over a period of 7.5 years up to April 4, 1989 and burned up in the Earth's atmosphere on March 5, 1991.
swell
- Quick Facts: Solar Mesosphere Explorer (SME) Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics
- SME in the NSSDCA Master Catalog (English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ SME in the Encyclopedia Astronautica , accessed April 2, 2016 (English).
- ^ The Solar Mesosphere Explorer - Instruments . University of Colorado
