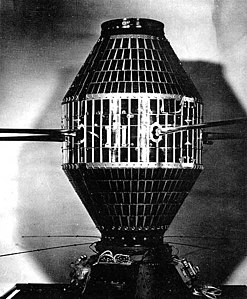
Explorer 20
| IE-A (Explorer 20) | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Type: | Research satellite |
| Country: |
|
| Operator: |
|
| COSPAR-ID : | 1964-051A |
| Mission dates | |
| Dimensions: | 44.5 kg |
| Begin: | August 25, 1964, 13:43 UTC |
| Starting place: | Vandenberg AFB SLC-5 |
| Launcher: | Scout-X4 |
| Flight duration: | 16 months |
| Status: | burned up |
| Orbit data | |
| Rotation time : | 104 min |
| Orbit inclination : | 79.9 ° |
| Apogee height : | 1,025 km |
| Perigee height : | 864 km |
| Eccentricity : | 0.01098 |
Explorer 20 , also known as IE-A referred to was a satellite of the United States , which on 25 August 1964, under the Explorer program started successfully.
begin
The satellite was on August 25, 1964 a Scout - carrier rocket from the Vandenberg Air Force Base into a low earth orbit brought.
mission
Mission objectives of Explorer 20 were the measurement of the electron distribution, the ion density and their temperature as well as the investigation of cosmic noise sources in the range between two and seven MHz.
The following measuring instruments were carried:
- an ion probe for altitudes between 300 and 1000 km
- a spectrometer to study the ions
- a receiver to investigate the noise sources
Since no recording device was carried, the data could only be transmitted to telemetry stations at close range. These stations were in Hawaii , Great Britain , Singapore , Africa and Australia . Despite difficulties due to interference , the experiments could be carried out for 16 months.
Whereabouts of the satellite
After the satellite no longer responded to radio commands from December 20, 1965, it remained in earth orbit.
See also
Web links
- Explorer 20 in the NSSDCA Master Catalog (English)
