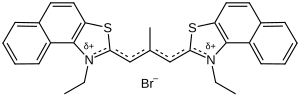
Stains-all
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Stains-all | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 30 H 27 BrN 2 S 2 | |||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 559.58 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Stains-all ( English colors everything , 1-ethyl-2- [3- (1-ethylnaphto [1,2- d ] thiazolin-2-ylidene) -2-methyl-propenyl] naphto [1,2- d ] thiazolium bromide ) is a carbocyanine dye that stains anionic proteins , nucleic acids , anionic polysaccharides and other anionic molecules.
properties
Stains-all has metachromatic properties, as it changes its color after binding to a negatively charged molecule depending on the contact. The detection limit for phosphoproteins is less than 1 ng after one hour of staining, for anionic polysaccharides between 10 and 500 ng. Strongly anionic proteins are colored blue, proteoglycans are colored purple, and anionic proteins are colored pink. Furthermore, RNA with a detection limit of 90 ng is colored blue-purple and DNA with a detection limit of 3 ng is colored blue. Stains-all is light-sensitive, which is why staining with Stains-all is carried out in the absence of light and then immediately documented photographically. The coloring of anionic proteins can be made permanent by a subsequent silver coloring , which can only be colored poorly with silver without pretreatment. The analogue Ethyl- Stains-all has similar properties to Stains-all, with differences in solubility and coloring properties.
Applications
Stains-all stains nucleic acids, anionic proteins, anionic polysaccharides such as alginic acid and pectic acid , hyaluronic acid and dermatan sulfate , heparin , heparan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate , among other things . It is therefore used in biochemistry for SDS-PAGE , agarose gel electrophoresis and in histology , e.g. B. for coloring growth lines in bones .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Alfa-Aesar: Safety data sheet H32127 , accessed on May 19, 2015.
- ^ MR Green, JV Pastewka, AC Peacock: Differential staining of phosphoproteins on polyacrylamide gels with a cationic carbocyanine dye. In: Analytical biochemistry. Volume 56, Number 1, November 1973, ISSN 0003-2697 , pp. 43-51, PMID 4128675 .
- ↑ JM Myers, A. Veis, B. Sabsay, AP Wheeler: A method for enhancing the sensitivity and stability of stains-all for phosphoproteins separated in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. In: Analytical biochemistry. Volume 240, Number 2, September 1996, ISSN 0003-2697 , pp. 300-302, doi : 10.1006 / abio.1996.0361 , PMID 8811925 .
- ^ Y. Sharma, CM Rao, SC Rao, AG Krishna, T. Somasundaram, D. Balasubramanian: Binding site conformation dictates the color of the dye stains-all. A study of the binding of this dye to the eye lens proteins crystallins. In: The Journal of biological chemistry. Volume 264, Number 35, December 1989, ISSN 0021-9258 , pp. 20923-20927, PMID 2480348 .
- ↑ WT Cong, WJ Ye, M. Chen, T. Zhao, ZX Zhu, C. Niu, DD Ruan, MW Ni, X. Zhou, LT Jin: Improved staining of phosphoproteins with high sensitivity in polyacrylamide gels using Stains-All. In: Electrophoresis. Volume 34, number 24, December 2013, ISSN 1522-2683 , pp. 3277-3286, doi : 10.1002 / elps.201300328 , PMID 24114871 .
- ↑ a b N. Volpi, F. Maccari, J. Titze: Simultaneous detection of submicrogram quantities of hyaluronic acid and dermatan sulfate on agarose-gel by sequential staining with toluidine blue and Stains-All. In: Journal of chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. Volume 820, Number 1, June 2005, ISSN 1570-0232 , pp. 131-135, doi : 10.1016 / j.jchromb.2005.03.028 , PMID 15866501 .
- ↑ a b N. Volpi, F. Maccari: Detection of submicrogram quantities of glycosaminoglycans on agarose gels by sequential staining with toluidine blue and Stains-All. In: Electrophoresis. Volume 23, Number 24, December 2002, ISSN 0173-0835 , pp. 4060-4066, doi : 10.1002 / elps.200290021 , PMID 12481260 .
- ^ A b H. A. Goldberg, KJ Warner: The staining of acidic proteins on polyacrylamide gels: enhanced sensitivity and stability of "stains-all" staining in combination with silver nitrate. In: Analytical biochemistry. Volume 251, Number 2, September 1997, ISSN 0003-2697 , pp. 227-233, doi : 10.1006 / abio.1997.2252 , PMID 9299020 .
- ↑ Data sheet Stains-All ~ 95% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on May 16, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ^ MR Green, JV Pastewka: The cationic carbocyanine dyes Stains-all DBTC, and Ethyl-Stains-all, DBTC-3,3 ', 9 triethyl. In: The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry: official journal of the Histochemistry Society. Volume 27, Number 3, March 1979, ISSN 0022-1554 , pp. 797-799, PMID 90067 .
- ^ AG Krishna, Y. Sharma: Conformation of alginate and pectate chains monitored by the binding of the dye stains-all. In: Indian journal of biochemistry & biophysics. Volume 28, Number 1, February 1991, ISSN 0301-1208 , pp. 30-33, PMID 1711507 .
- ↑ HE Gruber, P. Mekikian: Application of stains-all for demarcation of cement lines in embedded methacrylate bone. In: Biotechnic & histochemistry: official publication of the Biological Stain Commission. Volume 66, Number 4, 1991, ISSN 1052-0295 , pp. 181-184, PMID 1716999 .
