Styrene-butadiene rubber
| Structural formula | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
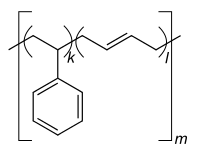
|
|||||||
| General | |||||||
| Surname | Styrene-butadiene rubber | ||||||
| other names |
Styrene-butadiene copolymer |
||||||
| CAS number | 9003-55-8 | ||||||
| Monomers / partial structures | |||||||
| properties | |||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||
|
|||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||
Styrene-butadiene rubber ( abbreviation SBR , derived from English styrene-butadiene rubber ; also styrene-butadiene copolymer , abbreviation SB ) is a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene . SBR is the most widely produced variant of synthetic rubber . In 2012 around 5.4 million tons were used worldwide.
history
The German chemists Walter Bock and Eduard Tschunkur were first able to manufacture it in 1929 with the help of emulsion polymerization . This made it the first commercially viable synthetic rubber . Under the name Buna-S , SBR was supposed to make the German war economy (1939–1945) independent of the import of natural rubber as part of the Heimstoff policy .
Manufacturing
For large-scale production, emulsion polymerization is used at 5 ° C., which is therefore also referred to as cold polymerization . Warm polymerization at approx. 50 ° C results in branched molecular chains that make the rubber obtained from it less elastic. In contrast, solution polymerization is used for rubber for winter tires, which is elastic even at low temperatures . Free-radical polymerization is also possible, but has not yet been used on an industrial scale. SBR usually contains 23.5% styrene and 76.5% butadiene. After the polymerization , the SBR is crosslinked by vulcanization and thus gets its final shape.
properties
SBR shows good resistance and little swelling in inorganic and organic acids and bases as well as in alcohols and water . It is insensitive to brake fluid , but is mostly replaced by EPDM .
On the other hand, it swells strongly in aliphatics , aromatics and chlorinated hydrocarbons , especially in mineral oil , lubricating grease and gasoline .
It is more resistant to the elements than natural rubber, but worse than z. B. Chloroprene rubber (CR) and ethylene-propylene-diene rubber (EPDM).
Thermal application range: approx. −40 ° C to +70 ° C.
use
SBR is the most widely used synthetic rubber today, which is used in the manufacture of tires - especially the treads -, seals and conveyor belts using various fillers such as silica .
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Arne Peters: Elastomer market with perspective. ( Memento of the original from July 14, 2014 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. Report in the K-Zeitung from June 24, 2013.
- ↑ K. Nusser, T. Mosbauer, GJ Schneider: Silica dispersion in styrene butadiene rubber composites studied by synchrotron tomography . Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, Volume 358, Issue 3 , Elsevier 2012.