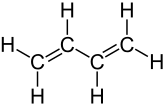
1,3-butadiene
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | 1,3-butadiene | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 4 H 6 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
colorless gas with an aromatic odor |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 54.09 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
gaseous |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
2.4982 kg m −3 (0 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
−108.92 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
−4.5 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Vapor pressure |
239.8 k Pa (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
slightly soluble in water (1.03 g l −1 at 20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4292 (−25 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| MAK |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Thermodynamic properties | ||||||||||||||||
| ΔH f 0 |
110.0 kJ / mol |
|||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
1,3-Butadiene [ -butaˈdi̯eːn ] ( vinylethylene ) is a colorless gas with a mild, aromatic odor. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon of great industrial importance. In addition, there is 1,2-butadiene , which is more difficult to produce and less important industrially .
2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene or isoprene , the basic unit of the terpenes , is a derivative of butadiene.
Manufacturing
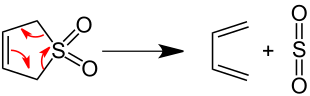
Butadiene is produced industrially in considerable quantities by splitting off hydrogen from saturated hydrocarbons through vigorous heating ( cracking ). In the laboratory, the decomposition of is 3-sulfolene in boiling xylene in a [4 + 1] - cycloelimination to 1,3-butadiene and sulfur dioxide used.
properties
The odor threshold of butadiene is 4 mg / m³. The gas can be easily liquefied. Butadiene is heavier than air and only very slightly soluble in water - at 1.03 g / l at 20 ° C.
Butadiene is flammable and polymerizes easily, which is why a stabilizer such as 4- tert- butylpyrocatechol (TBC) is usually added to it. The heat of polymerization is −73 kJ mol −1 or −1350 kJ kg −1 .
Conjugated double bonds in 1,3-butadiene
| Conjugated π-bond |
 Delocalized molecular orbital in 1,3-butadiene |
In the planar molecule, all four carbon atoms are sp 2 - hybridized . The π orbitals overlap above and below the molecular plane. π bonds are created by overlapping the 1st and 2nd carbon atoms and the 3rd and 4th carbon atoms. In addition, the orbitals of the 2nd and 3rd carbon atoms can overlap, so that the π electrons can spread over the entire molecule. The electrons are delocalized . Because electrons are distributed over a larger space, an increased stability is observed in 1,3-butadiene. The influence of these conjugated double bonds is evident in addition reactions of butadiene: 1,2- and 1,4-adducts can form. In the latter case, a "new" double bond is formed between the 2nd and 3rd atom. Polyaddition reactions of butadiene, which lead to 1,2-polybutadiene or 1,4-polybutadiene, proceed analogously , see butadiene rubber . The ratio of 1,4 to 1,2 linkage depends strongly on the polymerization method and the reaction conditions.
use
More than 90 percent of butadiene production is processed into synthetic rubber . Another application is ABS , a terpolymer made from acrylonitrile , butadiene and styrene . In addition, adiponitrile , which is an intermediate product in the production of polyamides, is produced on an industrial scale from butadiene and hydrogen cyanide . Butadiene is used to produce hydroxyl-terminated polybutadienes (HTPB), which are used as fuel in solid rocket engines. Cyclobutene can be obtained by photochemical cyclization of 1,3-butadiene:
However, this method only works with a 30% yield.
A mixture of 1,6-heptadiene and 1,5-heptadiene can be obtained by reaction with allyl magnesium bromide and diethyl ether , subsequent hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid and neutralization with sodium hydrogen carbonate .
Historical
That of butadiene and the catalyst sodium produced polymer Buna ( Bu tadien Na trium) had great importance for the German armaments and war economy before and during the Second World War.
safety instructions
Butadiene is extremely flammable. It forms explosive mixtures between an air volume fraction of 1.4 to 16.3 percent. Butadiene has a narcotic effect. 1,3-Butadiene is carcinogenic in humans . An increased number of cancers has been found in industrial workers who have been exposed to 1,3-butadiene for long periods of time . These were mainly lympho-haematopoietic malignancies ( malignant lymphomas and leukemias ).
In 2013, 1,3-butadiene was included in the EU's ongoing action plan ( CoRAP ) in accordance with Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 (REACH) as part of substance evaluation . The effects of the substance on human health and the environment are re-evaluated and, if necessary, follow-up measures are initiated. The cause of the uptake of 1,3-butadiene was concerns about its classification as a CMR substance. The reassessment took place from 2014 and was carried out by Germany . A final report was then published.
Occupational disease
Since August 2017, certain diseases caused by 1,3-butadiene can be recognized as occupational diseases in Germany upon application (number 1320 of Appendix 1 to the Occupational Diseases Ordinance - BKV). This also applies to illnesses that occurred before this date ( Section 6 (1) BKV).
literature
- J. Grub, E. Löser: Butadienes . In: Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Technical Chemistry . Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim 2012; doi : 10.1002 / 14356007.a04_431.pub2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on butadiene in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on February 1, 2016(JavaScript required) .
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, pp. 3-72.
- ↑ Entry on Buta-1,3-diene in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on February 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ Swiss Accident Insurance Fund (Suva): Limit values - current MAK and BAT values (search for 106-99-0 or 1,3-butadiene ), accessed on September 21, 2019.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Ed.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics . 90th edition. (Internet version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, FL, Standard Thermodynamic Properties of Chemical Substances, pp. 5-25.
- ^ Siegfried Hauptmann : Reaction and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry , BG Teubner, Stuttgart 1991, ISBN 3-519-03515-4 , p. 131.
- ↑ Trade Association Raw Materials and Chemical Industry , Leaflet R 008 Polyreactions and Polymerizable Systems , Edition 05/2015, ISBN 978-3-86825-069-5 .
- ↑ Waldemar Adam, Thomas Oppenlaender, Gerald Zang: The 185-nm photochemistry of cyclobutene and bicyclo [1.1.0] butane. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 107, 1985, pp. 3921-3924, doi: 10.1021 / ja00299a028 .
- ^ Albert Gossauer: Structure and reactivity of biomolecules , Verlag Helvetica Chimica Acta, Zurich 2006, ISBN 978-3-906390-29-1 , p. 143.
- ↑ Daniel Bellus, Chao-Jun Li, Teck-Peng Loh, Istvan Marko, Keiji Maruoka, Norikazu Miyoshi, Kunio Mochida, Ryoji Noyori, Masataka Oishi, Takashi Ooi, Susumu Saito, Makoto Shimizu, Tamotsu Takahashi, Sadao Tsuboi, Masahiko Yamaguchi, Hisashi Yamamoto, Akira Yanagisawa, Hajime Yasuda: Science of Synthesis: Houben-Weyl Methods of Molecular Transformations Vol. 7: Compounds of Groups 13 and 2 (Al, Ga, In, Tl, Be ... Ba) . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2014, ISBN 3-13-171771-8 , p. 569 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Butadiene chapter (PDF; 829 kB) of IARC monograph 97 from 2008, link accessed on February 14, 2012.
- ↑ 1,3-BUTADIENE - Risk Assessment Report. (PDF; 4.5 MB) European Commission, Joint Research Center, Institute for Health and Consumer Protection, European Chemicals Bureau, 2002.
- ^ European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Substance Evaluation Report and Conclusion Document .
- ↑ Community rolling action plan ( CoRAP ) of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA): Buta-1,3-diene , accessed on March 26, 2019.