Surfactin
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
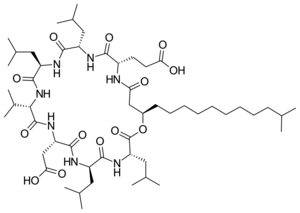
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Surfactin | |||||||||||||||
| other names |
3 - [(3 S , 6 R , 9 S , 12 S , 15 R , 18 S , 21 S , 25 R ) -9- (carboxymethyl) -3,6,15,18-tetraisobutyl-12-isopropyl-25 - (10-methylundecyl) -2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23-octaoxo-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22-heptaazacyclopentacosan-21-yl] propanoic acid ( IUPAC ) |
|||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 53 H 93 N 7 O 13 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
beige solid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 1036.34 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
|||||||||||||||
| solubility |
soluble in ethanol |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||||||||
Surfactin is a bacterial biosurfactant and biocide that is used as an antibiotic .
properties
Surfactin is a cyclic lipopeptide that is produced by Bacillus subtilis , among others . As the strongest known biosurfactant and suspected pore-forming toxin, surfactin destabilizes bacterial cell membranes at a mass concentration of 12 to 50 milligrams per liter, which triggers lysis of bacterial cells, sometimes also in mammalian cells. At a concentration of 20 micromolar, surfactin lowers the interfacial tension of water from 72 mN m −1 to 27 mN m −1 . Therefore, surfactin is also a virostat for some enveloped viruses.
The cyclic peptide Surfactin contains the amino acids L - glutamic acid , L - leucine , D -leucine, L - valine , L - aspartic acid , D leucine and L -leucine and a fatty acid of thirteen to fifteen carbon atoms. It is produced as a non-ribosomal peptide by a multi-enzyme complex .
Mechanism of Lysis
Three different mechanisms of destabilization of cell membranes have been proposed, membrane transport of cations through the cell membrane in the manner of a flip-flop , the formation of a pore in the membrane, and the lowering of the strength and increase of the permeability of biomembranes by the surfactant surfactin.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d Datasheet Surfactin, from Bacillus subtilis, ≥98% (HPLC and TLC) from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on January 6, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ↑ R. Sen: Surfactin: biosynthesis, genetics and potential applications. In: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology . Volume 672, 2010, pp. 316-323, PMID 20545293 .
- ↑ SC Baker, CY Chen: Enrichment and purification of lipopeptide biosurfactants. In: Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology . Volume 672, 2010, pp. 281-288, PMID 20545290 .
- ↑ H. Heerklotz, J. Seelig: Detergent-like action of the antibiotic peptide surfactin on lipid membranes. In: Biophysical Journal. Volume 81, Number 3, September 2001, pp. 1547-1554, doi : 10.1016 / S0006-3495 (01) 75808-0 . PMID 11509367 . PMC 1301632 (free full text).
- ↑ S. Dufour, M. Deleu, K. Nott, B. Wathelet, P. Thonart, M. Paquot: hemolytic activity of new linear surfactin analogs in relation to Their physico-chemical properties. In: Biochimica et Biophysica Acta . Volume 1726, number 1, October 2005, pp. 87-95, doi: 10.1016 / j.bbagen.2005.06.015 . PMID 16026933 .
- ↑ a b F. Peypoux, JM Bonmatin, J. Wallach: Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. In: Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology . Volume 51, Number 5, May 1999, pp. 553-563, PMID 10390813 .
- ↑ MS Yeh, YH Wei, JS Chang: Enhanced production of surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by addition of solid carriers. In: Biotechnology progress. Volume 21, Number 4, 2005 Jul-Aug, pp. 1329-1334, doi: 10.1021 / bp050040c . PMID 16080719 .
- ↑ M. Jung, S. Lee, H. Kim: Recent studies on natural products as anti-HIV agents. In: Current medicinal chemistry. Volume 7, Number 6, June 2000, pp. 649-661, PMID 10702631 .
- ↑ M. Deleu, O. Bouffioux, H. Razafindralambo, M. Paquot: Interaction of surfactin with Membranes: A Computational Approach. In: Langmuir. 19 (2003), pp. 3377-3385.
- ↑ H. Heerklotz, T. Wieprecht, J. Seelig: Membrane Perturbation oby the Lipopeptide Surfactin and Detergents as Studied by Deuterium NMR. In: J. Phys. Chem. (2004) 108, pp. 4909-4915.
- ↑ M. Deleu, O. Bouffioux, H. Razafindralambo, M. Paquot: Interaction of surfactin with Membranes: A Computational Approach. In: Langmuir. 19 (2003), pp. 3377-3385.
- ↑ M. Maire, P. Champeil, JV Moller: Interaction of Membrane Proteins and lipids with Solubilizing Detergents. In: BBA. (2000) 1508, pp. 86-111.