Taiwanese angel shark
| Taiwanese angel shark | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Squatina formosa | ||||||||||||
| Shen & Ting , 1972 |
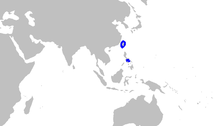
The Taiwanese angel shark ( Squatina formosa ) is a ground-dwelling shark found in the Pacific in the area of Taiwan and the northern Philippines .
Appearance and characteristics
The Taiwanese angel shark probably reaches a maximum body length of around 100 cm, but no adult animals have been described. As with other angel sharks, the body is strongly flattened with very broad pectoral fins , which makes the animals look more like long rays in shape . However, the pectoral fins are clearly separated from the trunk, while in most rays they merge seamlessly into the body. They have two dorsal fins and no anal fin . The body has a yellow-brown to brown back color with small, paired, darker eye spots . It also has small, light spots between the head and the first dorsal fin and numerous small and large dark spots spread over the body. They have saddle spots in the area of the dorsal fins . There are slightly enlarged thorns on the snout area and in other head areas. The young animals also have thorns on their backs in a row along the center line.
The eyes are on the top of the head with a concave surface between the eyes, the mouth is terminal, the outer nostrils are provided with short barbels . The injection holes are large and a distance less than the length of the eye from the eyes. The number of lateral, lower gill openings is five. The nasal flaps and barbels are only slightly fringed or have smooth edges.
distribution
The range of the Taiwanese angel shark is in the coastal area of the Pacific in the area of Taiwan and the northern Philippines . It lives on the outer edge of the continental shelf , mainly at depths between 180 and 385 meters.
Way of life
Little data is available on the way the Taiwanese angel shark lives. Like other angel sharks, it probably feeds mainly on small bony fish, molluscs and crustaceans , which it prey on lying on the ground as a lurker . Like all angel sharks, it is ovoviviparous - the eggs are hatched in the mother before the young are born alive. The length of the young sharks is about 33 centimeters at birth.
The animals reach sexual maturity with a body length of more than 46 centimeters (so far no sexually mature animals have been described).
Danger
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies this shark as endangered ("Endangered"). The shark is not targeted, but is mainly caught as by-catch in bottom and trawling fisheries that are carried out throughout its range; individual individuals have been found in fish markets in northern Taiwan. The classification as an endangered species was made despite the poor knowledge of the species by comparison with other angel sharks, in which population declines of more than 80% were proven for areas with high fishing pressure.
supporting documents
- ↑ a b Squatina formosa in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2010. Posted by: Walsh, JH & Ebert, DA, 2008. Accessed on December 18 of 2010.
literature
- Leonard Compagno , Marc Dando, Sarah Fowler: Sharks of the World . Princeton University Press , Princeton and Oxford 2005, p. 142. ISBN 978-0-691-12072-0
Web links
- Taiwanese angel shark on Fishbase.org (English)