Tennant Creek
| Tennant Creek | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Main Street |
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
|||||||
|
|
|||||||
Tennant Creek is a place located directly on the Stuart Highway in the Australian Northern Territory . It was founded around 1860 and has a population of around 3,000. Tennant Creek is located approximately 1,000 km south of the state capital Darwin and approximately 500 km north of Alice Springs . The city got its name from a nearby watercourse of the same name. It is the administrative center and the largest town in the Barkly region .
history
In 1860, out of gratitude , John McDouall Stuart named this watercourse after John Tennant, a South Australian cattle breeder. Tennant had co-financed Stuart's expedition to Australia. In 1872 a makeshift telegraph station was built. Two years later, when the Tennant Creek Overland Telegraph Station was completed, telegraph traffic was relocated here. It was not until 1930, when a short but violent gold rush broke out, that the place gained fame. The nickname Heart of Gold (German: Goldherz ) also comes from that time . Copper and gold are still mined here today . During the Second World War , there was a hospital near Tennant Creek and the airport was used as an emergency airport.
In February 2009, Tennant Creek gained worldwide media attention when a family quarrel turned into a street battle with more than 100 participants. According to reports from the police, the opponents brandished axes and knives and attacked each other with batons and boomerangs. A 63-year-old woman suffered serious injuries and was flown to a hospital in Alice Springs.
climate
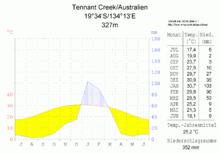
Tennant Creek has a hot desert climate ( climate classification according to Köppen and Geiger : BWh). Nevertheless, a long-term average of 468.4 mm of rain falls per year and a clear distinction can be made between dry and rainy seasons. The latter ranges from December to March; This is the period during which most of the annual precipitation falls and temperatures reach their maximum values. The drier months are characterized by lower temperatures, lots of sun (an average of 9.8 hours of sun per day) and mild nights. The prevailing wind direction is east to southeast.
The highest temperature ever recorded was 45.4 ° C and was recorded on December 2, 2007; the lowest with 4.5 ° C on July 14, 1978.
|
Average monthly temperatures and rainfall for Tennant Creek Airport
Source: Australian Bureau of Meteorology : Tennant Creek Airport Station. Observation period: 1969–2013. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Attractions
The city is increasingly profiling itself as a tourist destination. She not only focuses on the search for gold, but also on the way of life of the Aborigines . The Kaytetye Aborigines live in the area around Tennant Creek, who hold a Native Title for land and water in the south and southeast of Tennant Creek.
Gold mining
Veteran gold digger Colonel Bremner takes visitors to his old Dot Mine . In the evening he tells the visitors about the old times around the campfire.
An old gold processing facility, Gold Stamp Battery , has been restored and refurbished and is now a tourist attraction. The system is switched on during guided tours. Nearby is the lookout in the Nobles Nob Mine , which was the largest Australian gold mine until it was closed in 1985.
53 km northwest of Tennant Creek is the abandoned Moonlight Rockhole Fossicking Area near the mining town of Warrego. Everyone can mine gold and look for nuggets here, provided they have a miners right .
National Trust Museum
The local history museum shows a colorful mixture of exhibits from the area. It is housed in a former auxiliary hospital that was built by the army in 1942.
Overland Telegraph Station
The former telegraph station from 1872 is now a museum and one of Tennant Creek's most famous attractions. It is located directly on the Trans- Australian Telegraph Line , with the help of which Australia was once connected to the world.
Devil's Marbles
Devil's Marbles - the strange rock formations about 110 km south of Tennant Creek on the Stuart Highway , which consist of thousands of weathered and rounded granite rocks between 3 and 5 meters high , are called the devil's marbles . The Kaytetye Aborigines, who they call Karlu Karlu , think they are the eggs of the rainbow snake they adore from the dreamtime . The place is an important spiritual place for the Kaytetye. The rounded rocks were eroded over thousands of years by wind, sand, temperature differences and rain and thus brought into their present form.
Picture gallery
Central Australian Railway at Tennant Creek
Web links
- The City website (English)
Individual evidence
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics : Tennant Creek ( English ) In: 2016 Census QuickStats . June 27, 2017. Retrieved April 5, 2020.
- ↑ Axes, knives and boomerangsKleiner - family dispute escalates. Article on “ntv.de” from February 24, 2009, accessed on February 24, 2009.
- ^ A b c Australian Bureau of Meteorology : Tennant Creek Airport Station. Observation period: 1969–2013. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- ↑ http://www.austlii.edu.au/au/journals/AILR/2004/12.html