Trifunctional purine synthesis protein
| Trifunctional purine synthesis protein | ||
|---|---|---|
|
||
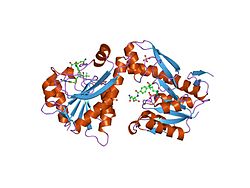
| Representation based on PDB 1rbm | ||
|
Existing structural data : 1MEJ , 1MEN , 1MEO , 1NJS , 1RBM , 1RBQ , 1RBY , 1RBZ , 1RC0 , 1RC1 , 1ZLX , 1ZLY , 2QK4 , 2V9Y , 4EW1 , 4EW2 , 4EW3 |
||
| Properties of human protein | ||
| Mass / length primary structure | 1009 amino acids | |
| Cofactor | Mn 2+ | |
| Isoforms | long, short (433 aa) | |
| Identifier | ||
| Gene names | GART AIRS; GARS; GARTF; PAIS; PGFT; PRGS | |
| External IDs | ||
| Enzyme Classifications | ||
| EC, category | 6.3.4.13 , ligase | |
| Response type | Addition of glycine | |
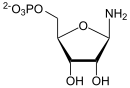
| Substrate | 5-phosphoribosylamine + ATP + glycine | |
| Products | Glycine amide ribonucleotide + ADP + P i | |
| EC, category | 2.1.2.2 , transferase | |
| Response type | Transfer of a formyl residue | |
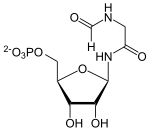
| Substrate | Glycine amide ribonucleotide + N 10 -THF | |
| Products | Formylglycine amide ribonucleotide + THF | |
| EC, category | 6.3.3.1 , ligase | |
| Response type | Ring closure | |
| Substrate | Formylglycine amidine ribonucleotide + ATP | |
| Products | 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide + H 2 O + ADP + P i | |
| Occurrence | ||
| Parent taxon | Creature | |
| Orthologue | ||
| human | House mouse | |
| Entrez | 2618 | 14450 |
| Ensemble | ENSG00000159131 | ENSMUSG00000022962 |
| UniProt | P22102 | Q64737 |
| Refseq (mRNA) | NM_000819 | NM_010256 |
| Refseq (protein) | NP_000810 | NP_034386 |
| Gene locus | Chr 21: 33.5 - 33.54 Mb | Chr 16: 91.62 - 91.65 Mb |
| PubMed search | 2618 |
14450
|
The trifunctional purine synthesis protein (GARS-AIRS-GART) (also adenosine-3 ) is an enzyme in animals in which three different enzymatic domains are fused to form a protein: phosphoribosylamine glycine ligase (GARS), phosphoribosylglycine amide formyl transferase (GART ) and the phosphoribosylformylglycine amidine cyclo-ligase (AIRS). These activities are part of purine biosynthesis and occur in all living things: as single enzymes in prokaryotes and as partially bifunctional enzymes in yeast .
The domains of adenosine-3 are arranged linearly and catalyze steps 2, 5, and 3 of the ten-step biosynthesis of IMP . The genetic locus in humans for the adenosine 3 gene GART is on chromosome 21 , which is possibly the cause of elevated purine levels in Down syndrome .
Catalyzed reactions
GARS
The phosphoribosylamine glycine ligase domain facilitates the addition of glycine to 5-phosphoribosylamine (PRA) to form glycine amide ribonucleotide (GAR).
GART
Phosphoribosylglycine amide formyltransferase (GART) catalyzes the formylation of glycine amide ribonucleotide (GAR) to formylglycine amide ribonucleotide (FGAR) using formyl tetrahydrofolate .
AIRS
The phosphoribosylformylglycine amidine cyclo-ligase domain cyclizes formylglycine amidine ribonucleotide (FGAM) to 5-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide (AIR).
Individual evidence
- ↑ UniProt P22102
- ↑ D. Banerjee, K. Nandagopal: Phylogenetic analysis and in silico characterization of the GARS-AIRS-GART gene which codes for a tri-functional enzyme protein involved in de novo purine biosynthesis. In: Molecular biotechnology. Volume 42, Number 3, July 2009, pp. 306-319, doi : 10.1007 / s12033-009-9160-1 . PMID 19301155 .
- ↑ D. Patterson, S. Graw, C. Jones: Demonstration, by somatic cell genetics, of coordinate regulation of genes for two enzymes of purine synthesis assigned to human chromosome 21. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 78, Number 1, January 1981, pp. 405-409, PMID 6941256 . PMC 319062 (free full text).