Union Canal (Scotland)


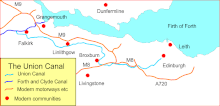
The Union Canal is a shipping canal in Scotland . It branches off the Forth and Clyde Canal at the Falkirk Wheel and leads from there to Edinburgh .
history
Construction of the Union Canal began in 1817 to connect the capital Edinburgh to the Forth and Clyde Canal, which crosses central Scotland between the Clyde and Forth rivers . The opening took place in 1822. The main transport goods were building materials and coal towards the growing capital Edinburgh. In the opposite direction, however, the capacity utilization of the canal boats was low. The railway between Glasgow and Edinburgh was opened as early as 1842, and it was a strong competitor to canal shipping. Passenger traffic on the canal was stopped as early as 1848. The facility fell into disrepair, and in the 1930s the lock staircase in Falkirk was demolished and backfilled, cutting off the canal for traffic. In 1965, the canal, which was no longer navigable, was officially declared abandoned.
In the 1990s, a rethink began to preserve and revitalize the historic canal routes and make them publicly used for tourism. As part of the Millennium Link project , the Forth and Clyde Canal and the Union Canal were restored and made passable again. The upper canal section was opened in 2001, and since the opening of the Falkirk Wheel in May 2002, the canal has been connected to the Forth and Clyde Canal again after almost seven decades.
Course and dimensions
The channel is a branch channel . As a “contour canal”, it always follows the terrain contour at the same height line and therefore manages with very few locks for a large part of its course, after it has quickly reached the height of its apex posture at its western beginning . It begins at the junction from the Forth and Clyde Canal ( here ), followed immediately by the entrance lock into the outer harbor basin and the Falkirk Wheel lift , which overcomes a height difference of 24 m. Immediately after the Falkirk Wheel there is a trough bridge and the Rough Castle Tunnel , which crosses under the Antonine Wall . After exiting the tunnel, the canal turns to the east. There is still a double lock ( Falkirk Wheel Top Locks 1 and 2 ) uphill to pass before the apex position is reached, which extends to the end of the canal in Edinburgh without further locks. From the historical opening until the 1930s, this ascent was accomplished by a lock staircase with eleven locks - near the current location of the Falkirk Wheel - which covered a height difference of 33.50 m over a 1.5 kilometer stretch. The 633 m long Falkirk Tunnel follows in the city of Falkirk . On the border of the Council Areas Falkirk and West Lothian the channel crossing on the 247-meter Avon Aqueduct , a canal bridge , the River Avon . The Almond Aqueduct crosses the Union Canal over the River Almond on the border between the Council Areas West Lothian and Edinburgh. The canal ends today at Lochrin Basin in the Edinburgh Quai district in the Lochrin district to the southwest of the old town ( here ).
Today the canal is about 50 km long. It is designed for the typical narrowboats .
literature
- Jean Lindsay: The Canals of Scotland . David & Charles, Newton Abbot 1968, ( The Canals of the British Isles ).
- From Sea To Sea: A History of the Scottish Lowland and Highland Canals , Glasgow 2005, ISBN 1-903238-94-3
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ The Union Canal - Cheap Coal for the Capital , English, accessed October 23, 2015
- ↑ History of the Union Canal on Scottish Canals , English, accessed October 24, 2015