Falkirk Wheel
The Falkirk Wheel is a modern boat lift near the Scottish city of Falkirk , which is unique in the world due to its construction in the manner of a Ferris wheel .
history
Roman times

The Roman Antonine Wall runs close to the Falkirk Wheel , which has been largely removed or destroyed by erosion over time, but is still visible as a terrain formation. The Roman Fort Rough Castle also stood here.
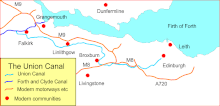
Original course of the canal
Since 1790 the Forth and Clyde Canal has traversed central Scotland in a west-east direction between the rivers Clyde and Forth . The Union Canal , opened in 1822, branches off to the west of Falkirk , an approx. 50 km long branch canal that ends at its eastern end directly in the city center of Edinburgh . The difference in height between the two positions is in the vicinity of the location of the Falkirk Wheel originally by a lock staircase of eleven locks km over a distance of 1.5 with a height difference of 33.50 m overcome. However, these locks fell into disrepair with the decline of the canal system due to competition from the railways and road traffic until they were backfilled in the 1930s.
New building

The old canal route was built and filled in in several places. The situation at Falkirk was particularly challenging, where the old lock staircase was built with a road through a residential area (Glenfuir Road / Greenbak Road). Therefore, a new route had to be found, which had to cross a railway line and the ground monument of the Antonine Wall without disturbing them and had to overcome the height difference of 33.5 m.
In the 1990s a project to revitalize the canals was started. The elevator, the construction of which began in 1998 and which has been connecting the canals again since then, is part of this project called Millennium Link , which comprised several measures on the two canals. The Falkirk Wheel was opened on May 24, 2002 by Queen Elizabeth II on the occasion of her golden jubilee on the throne . The cost of the new project amounted to 17 million pounds . The Antoninuswall is crossed under in the upper water of the Wheel by the Rough Castle Tunnel .
meaning
The canal and lifting system is primarily of tourist and water sports importance when traveling with smaller, narrow ships, the narrowboats , between Glasgow and Edinburgh . The lower Forth and Clyde Canal leads east to the Forth and west to the Clyde. It is connected to the outer harbor basin via a lock, the underwater area of the Falkirk Wheel. The higher Union Canal begins at the trough bridge of the Falkirk Wheel with the upper basin, which is directly connected to the Rough Castle Tunnel , and leads east to Edinburgh after a double lock (Falkirk Wheel Top Locks 1 and 2) that is still operationally part of the facility. The 147 m long canal tunnel crosses under the Antonine Wall and the Glasgow to Edinburgh railway via the Falkirk Line , one of the four rail connections between Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Technology and functionality
The entire structure has a diameter of over 35 meters and a mass of 1,800 tons . The height difference between the waterways is 24 meters.
Two water-filled troughs are arranged at their ends in two opposite arms of a wheel hub with a horizontal axis of rotation. The troughs lie parallel to the axis of rotation in circular sections of the boom and are rotated in them by a gear mechanism so that they maintain their horizontal position while the wheel is rotating.
The narrowboats to be transported enter these troughs under their own power through folding gates , which are then sealed watertight, and swim in the water filling of the trough during the ascent or descent (“ wet pumping ”). A half turn of the wheel to cope with the difference in altitude takes about four minutes. As soon as the wheel reaches a position in which the outriggers are aligned vertically with the troughs, the troughs are at the level of the upper or lower water, and the folding gates are opened for exit. The lower entrance and exit is on the north side from the outer harbor basin. The wheel is connected to the upper water to the south by a trough bridge, the other bridge piers of which take up the shape of the wheel and the storage pylons.
The axis of rotation is mounted in two reinforced concrete pylons, the slope side also accommodating the drive technology and at the same time forming the abutment of the trough bridge of the upper water at its upper end. The storage pylons do not stand directly in the water of the lower outer harbor basin, but in a "dry" concrete tub. The lower trough in each case also passes through this dry tub below the water level of the basin and, apart from the open folding gate to the entrance and exit, does not come into direct contact with the water.
balance
The wheel works on the principle that the drive does not have to lift two gondolas of the same weight , but only has to overcome friction . The work to lift the gondola going up is done by the gondola going down, the wheel is always in balance. The weight of a gondola does not depend on whether there is a boat in it, because due to the Archimedean principle , a floating boat displaces the amount of water that corresponds to its own weight.
The construction, however, reacts sensitively to level differences. Each of the gondolas has around 200 m² of water, so one centimeter of water corresponds to a mass of around two tons. In order to stay within the performance limits of the drive, the water levels of the two gondolas may differ by a maximum of 1.7 cm (according to other sources: 7.5 cm). To ensure this, a pump system with around 20 times the power of the wheel drive was installed at the upper lock point at Falkirk Wheel Top Locks , which regulates the level of the headwater (tunnel, upper fore basin, trough bridge and open upper trough) to match the underwater.
The physical work to be done or done consists in principle of scooping water or (unusable) generation of hydropower.
drive
The torque for turning the wheel is generated by a set of ten hydraulic motors which are arranged in two groups of five concentrically around the axis of rotation in the rear, landside pylon (hub carrier). The operating rooms for the hydraulic pumps, the emergency power supply and a transformer room are located in the pylon below the storage of the wheel. The hydraulic motors each work via an internal reduction in the ratio of 1: 100 by means of a drive pinion on a toothing of the rear bearing attached to the inner ring and only consume the relatively small amount of electricity of 1.5 kWh per lifting process. The two three-row rolling bearings with a diameter of four meters are custom-made by SKF .
Funding troughs
The gondolas each have 50 tons of empty weight and hold approx. 300 tons of water; They are 21.33 m long, 6 m wide, 1.37 m deep and 2.74 m clear entrance height, which can be used for boats.
Between the rear pylon and the back of the slope-side arm of the wheel there is a gear set which, similar to a planetary gear , ensures that the troughs remain in their relative horizontal position during the rotation. For this purpose, two smaller intermediate gears, mounted on the rotating boom, roll on an inner wheel that is arranged coaxially around the axis of rotation and firmly connected to the pylons, and transfer the position to outer gear rims that are connected to the troughs and have the same number of teeth as the inner wheel.
Trough gates
Both the troughs and the canal aqueduct above and the entrance from the forecourt below are closed by hydraulically operated folding gates before the troughs undock and the wheel is set in motion. These gates are posted on the ground, when open they lie in recesses in the bottom of the water. When closed, they fold up towards each other and appear above the water level. The narrow space between the trough and landside gate is then filled or pumped out via pipes. As long as the troughs are in the entry or exit position, they are fixed in the direction of the respective door by a hydraulic locking hook, on the other hand a sealing frame is hydraulically pressed against the trough to seal the gap. The water from the space in between is pumped into the respective other section, so there are no significant water losses. However, as part of a lock system (the next lock is around 500 meters away), the wheel must show exactly the total water consumption of the other locks. To do this, the amount of water not required by the wheel is bypassed.
Others
In the meantime, the Falkirk Wheel has also become a popular destination for tourists from near and far who are not self-driving. In addition to a tourist information office, there is a typical local restaurant and a small amusement park has been created in the immediate vicinity of the outer harbor basin.
Web links
- The Falkirk Wheel (English; official site)
- Undiscovered Scotland
- The Falkirk Wheel tourist guide
- Falkirk wheel
- The Falkirk Wheel at km 42 in Spiegel online
- Lifting process in real time on YouTube
Coordinates: 55 ° 59 ′ 57 ″ N , 3 ° 50 ′ 29 ″ W.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Rough Castle on undiscoveredscotland.co.uk
- ^ The Union Canal - Cheap Coal for the Capital , English, accessed October 23, 2015
- ↑ Information on the story on thefalkirkwheel.co.uk
- ^ The Millenium Link - Canal Facts , English, accessed October 23, 2015
- ↑ Article on the construction of the Rough Castle Tunnel, PDF file in English ( memento of the original from September 14, 2015 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was automatically inserted and not yet checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. , accessed October 21, 2015
- ↑ http://www.thefalkirkwheel.co.uk/about-the-wheel-/how-does-it-work on thefalkirkwheel.co.uk
- ↑ [1] on thefalkirkwheel.co.uk
- ↑ Buses, Elephants, & Kettles - The strange world of Falkirk Wheel Statistics , English, accessed October 23, 2015
- ↑ Falkirk Wheel Drive Chamber Visit - Description of the drive technology , English, accessed on October 21, 2015
- ↑ Where there's a wheel there's a way , SKF publication , PDF file, English speaking, accessed on October 23, 2015
- ↑ FAQ on the Falkirk Wheel , English, accessed on October 21, 2015
- ↑ Falkirk Wheel - Doors and Seals Description of the door mechanisms and the seals , English language, accessed on October 21, 2015