VIA Isaiah microarchitecture
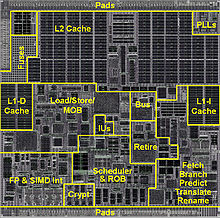
The VIA Isaiah microarchitecture is a newly developed superscalar processor architecture with out-of-order execution from Centaur Technology , a subsidiary of VIA Technologies . It differs from the architecture of the previous processors, for example that of the VIA C7 and also from the Intel Atom micro- architecture . The first processor to use it is the VIA Nano .
With the Isaiah architecture, VIA is introducing support for AMD64 in its own CPUs for the first time . The larger cache compared to the C7 architecture (2 × 64 kB L1 and 1 × 1 MB L2 cache) works exclusively, which means that data is stored either in the L1 or in the L2 cache, but not in both at the same time as is the case, for example, with processors from Intel . This effectively increases the size of the cache.
In addition, encryption was integrated into the architecture, the so-called VIA PadLock Engine .
future
The next development step was the introduction of a new socket and a dual-core processor in 2009. At the beginning of 2011, a quad-core processor based on the architecture was presented to the public.
Web links
- The VIA Isaiah Architecture (English)
- VIA Isaiah Architecture Introduction (PDF; 2.4 MB; English)