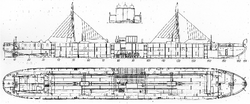
Vandal (ship)
|
Three-sided rift of the vandal
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
The Vandal was built in 1902/03 at the Sormovo shipyard and was the world's first diesel motor ship and diesel-electric ship . The test drive took place in the spring of 1903 about 4 months before the converted Petit Pierre barge .
Branobel
The Swedish engineer Gustav Robert Carlsund (1865-1958), who was in the service of Branobel under the direction of Emanuel Nobel - the nephew of Alfred Nobel , a Russian oil magnate - informed his employer about the "Rational Heat Engine" given by Rudolf Diesel . Emanuel Nobel, the large parts of the oil fields in Baku included (Branobel) was very interested in a marketing of oil and oil products.
Emanuel Nobel's father, Ludvig Nobel , had a steamer with superstructures arranged amidships built in Sweden in 1878. Below that were the engine room with the steam engine and the boiler room. 21 cylindrical cistern tanks were installed for the cargo oil. The finished ship, the Zoroaster , was then dismantled again and transported to Baku by inland barges via canals, the Volga and the Caspian Sea . Here the tanker was reassembled and put into operation for transport from Baku to Astrakhan. Later the standing cistern tanks were removed and the empty holds were used as tanks. With these conversion measures, the Zoroaster became one of the first modern oil tankers. The Zoroaster was later sunk with other ships and formed the foundation of the Neft Daşları oil island . The Zoroaster II with around 2000 tdw was built in 1911/12 for Branobel as a tanker with diesel drive.
From Astrakhan the oil and oil products were distributed with smaller steamers across the Volga to St. Petersburg and from here to the Baltic ports. The mechanical engineer Gustav Robert Carlsund and the shipbuilder Karl Wilhelm Hagelin (1860–1954), who started at Branobel in 1879 and was responsible for the Volga fleet, wanted to operate these transports with more modern, economical ships with diesel engines.
In 1898 R. Diesel issued the licenses to Nobel and Lamm
On January 25, 1898, Wallenberg and Oscar Lamm redeemed a license option for the Atlas works (now Atlas Copco). You signed the license agreement with Diesel in Munich. For 100,000 Swedish kroner (SEK; 1 SEK about 1.15 marks) they could build and sell diesel engines in Sweden. In the same year, Atlas founded AB Diesels Motorer in Sickla
In February 1898 Nobel and Wallenberg went to Berlin . Here at the Hotel Bristol, he acquired with his banker Marcus Wallenberg Laurentius Rudolf Diesel and his agent Berthold Bring the diesel engine - patents for Russia and paid a total of 800,000 marks. 600,000 marks were paid in cash and 200,000 marks for shares in the newly founded company Russische Dieselmotor, GmbH based in Nuremberg
In 1900 Hagelin became President of Branobel's Board of Directors. In 1902 he developed a concept for shipping oil over a 2,900-kilometer route from the Lower Volga to St. Petersburg and Finland and was instrumental in the design and construction of the Vandal at the Sormowo shipyard in Nizhny Novgorod .
construction
In 1902/03, the shallow river tanker for the transport of petroleum products was built at the Sormowo shipyard in Nizhny Novgorod on the Volga . The Vandal was around 75 meters long and 9.50 meters wide. She had a lifting capacity of 820 tons.
The engine room was in the middle of the ship between the forward and aft oil tanks. In January 1903, three cross-headless diesel engines (plunger piston engines) of the type K 3 III with 120 hp, known as K engines, were shipped from the Swedish Aktiebolag Diesel Motorer in Sickla near Stockholm (subsidiary of Atlas) to St. Petersburg for installation in the Vandal. The background was the Swedish further development carried out by Jonas Hesselman of the original MAN engines with crossheads (specific weight 220 kg / hp), which were also still being built in St. Petersburg, into crossheadless engines with a specific weight of 126 kg / hp. This saved around 11,300 kg per engine.
These motors powered electric generators from ASEA , which supplied the electricity for the electric drive motors in the aft section. By means of an electrical control, the electrical energy provided by the diesel engines and transmitted to the stern by cables was directed to the electric motors in such a way that forward and reverse travel at speeds between 30 and 300 rpm was possible.
In the spring of 1903 the Vandal made its maiden voyage from St. Petersburg over the Neva past the Schluisselburg to Lake Lagoda.
In 1904 the sister ship Sarmat was put into service, she received the meanwhile improved lighter engines without crosshead of the machine and arms factory "Ludvig Nobel" in St. Petersburg.
After 1903, Branobel had around 60 diesel-powered ships built or converted and by 1913 had the largest tanker fleet in the world.
See also
- Moses (ship) Branobel tanker with steam engine
- Petrolea Branobel tanker with steam engine
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c Lyle Cummins: Diesel`s engine: Chapter 10, Next Generation Engines, The Vandal . Carnot Press, Wilsonville 1993, pp. 281, 282 .
- ^ Vandal - 1903, pioneer ship with diesel engine drive for oil transport; Chapter 2. Emanuel Nobel purchases engine licenses for Russia at hochhaus-schiffsbetrieb.jimdo.com, accessed on May 20, 2019