Vinyl phosphonic acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
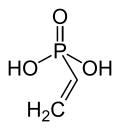
|
||||||||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Vinyl phosphonic acid | |||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | CH 2 = CHP (O) (OH) 2 | |||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
light yellow liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 108.03 g mol −1 | |||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
liquid |
|||||||||||||||
| density |
1.37 g cm −3 (20 ° C) |
|||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
36 ° C |
|||||||||||||||
| Refractive index |
1.4735 |
|||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . Refractive index: Na-D line , 20 ° C | ||||||||||||||||
Vinylphosphonic acid is an inorganic chemical compound from the group of phosphonic acid derivatives .
Extraction and presentation
The compound can be made in several ways, the most common of which consists in the addition of phosphorus trichloride to acetaldehyde and the reaction of the intermediate with acetic acid , followed by dehydrochlorination:
The preparation from vinylphosphonic acid dichloride or from 2-acetoxyethanephosphonic acid dialkyl esters is also possible.
properties
Vinylphosphonic acid is a clear, viscous, light yellow liquid.
use
Vinyl phosphonic acid is used as a flame retardant and in adhesives. It is also used in photolithography for the production of aluminum printing plates .
Vinylphosphonic acid polymers are homopolymers and copolymers of the compound with a characteristic side chain. They belong to the group of vinyl polymers and are usually water-soluble as (sodium) salts. The homopolymer ( polyvinylphosphonic acid ) is a polyacid and can be used as a primer for metals to increase the corrosion resistance and the adhesive strength of coating compounds or as a product with an anti-caries effect in dental compounds.
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g data sheet Vinylphosphonic acid, 97% from Sigma-Aldrich , accessed on September 21, 2015 ( PDF ).
- ^ A b R. Edmundson: Dictionary of Organophosphorus Compounds . CRC Press, 1987, ISBN 0-412-25790-4 , pp. 876 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Lavinia Macarie, Gheorghe Ilia: Poly (vinylphosphonic acid) and its derivatives . In: Progress in Polymer Science . tape 35 , no. 8 , August 1, 2010, p. 1078-1092 , doi : 10.1016 / j.progpolymsci.2010.04.001 ( sciencedirect.com ).
- ↑ Patent EP0061115 : Process for the production of vinylphosphonic acid. Registered on March 15, 1982 , published on May 30, 1984 , applicant: Hoechst AG, inventor: Hans-Jerg Kleiner.
- ^ Christoph Janiak, Hans-Jürgen Meyer, Dietrich Gudat, Ralf Alsfasser: Riedel Modern Inorganic Chemistry . Walter de Gruyter, 2012, ISBN 978-3-11-024901-9 , p. 627 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Entry on vinyl phosphonic acid polymers. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on September 21, 2015.



