YIG filter
A YIG filter is an adjustable electrical filter for microwaves with a high quality factor and a narrow band pass that can be adjusted over several octaves . It is used in spectrum analyzers , as a phase shifter or as a resonator of an adjustable oscillator .
Layout and function
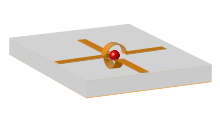
The basic structure of the filter consists of an approx. 0.5 mm large, polished, monocrystalline ball made of the ferrimagnetic material yttrium-iron-garnet (YIG), from which it is named , which is surrounded by two curved striplines that are turned by 90 ° against each other .
In the simplified sketch opposite, the YIG sphere is shown in red, the striplines run above or below the sphere. Of the two strip lines - each of which represents half a turn through the arc of a circle - one line serves as a signal input, the second line as a signal output for the filter. Due to the orthogonal structure, microwave energy can only pass from one line to the second if the orthogonality of the alternating magnetic field is disturbed. This happens through the precession motion of the electron spins of the ferrimagnetic YIG single crystal. The precession frequency is determined very precisely by an external static magnetic field. For this is in the immediate vicinity of the YIG sphere a not shown in the sketch electromagnet in the form of an electric coil that of direct current flowing through it. The setting range of the center frequency of the filter extends from 1.8 GHz to 6 GHz, for example .
Since the YIG filter is sensitive to changes in temperature, the entire arrangement is heated during operation and kept at a constant operating temperature of, for example, 85 ° C via a controller.
In the practical construction, the ball made of yttrium-iron-garnet is held by a dielectric holder in the center of the two conductor arcs. For example, it consists of beryllium oxide ceramic for good heat conduction .
The magnetic flux can also be generated by a permanent magnet . Even with electrical excitation, the magnetic field can only be changed relatively slowly. The reason is the inductance of the magnet coil and the material of the magnetic yoke. A second coil can therefore be used for faster controllability, which only causes a small stroke in the magnetic flux density.
Several YIG filters can be connected in series or in parallel if required .
The YIG resonator represents a circuit variation in which an adjustable YIG filter is part of an oscillator in order to generate an adjustable oscillator frequency.
literature
- J. Helszajn: YIG Resonators and Filters . John Wiley & Sons, 1985, ISBN 0-471-90516-X .
Web links
- YIG filters and oscillators, Wire Bonding. Retrieved November 21, 2014 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b YIG tuned filters. (PDF) (No longer available online.) Micro Lambda Wireless, archived from the original on March 3, 2016 ; Retrieved November 19, 2014 . Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ a b http://www.sjsu.edu/people/raymond.kwok/docs/project172/EE172_YIG_oscillator.pdf Donald Benson, Ali Tatari, Amaaduddin: YIG Oscillator , student thesis at San José State University 2009, accessed on 14 Jan. 2019