Bandpass

As a band-pass (including bandwidth filter ) is in the electrical engineering , audio engineering and optics , a filter called, the only signals of a frequency band can happen. The frequency ranges below and above the pass band are blocked or significantly weakened. A bandpass is the counterpart to the bandstop .
Depending on the area of application, these are optical , acoustic or electrical bandpass filters. A special, narrow-band electrical band pass is the band filter , which is used, among other things, for channel separation in heterodyne receivers .
properties
A bandpass can be created in the following ways:
- Series connection of a high-pass with a low-pass with clearly different cut-off frequencies ('improper band-pass'), if a relatively wide pass band is desired. The slope is then defined solely by the characteristics of the high and low pass. An example of this is the loudspeaker crossover branch for the midrange driver in a three-way loudspeaker box .
- one or more more or less damped resonant circuits with inductance (coil) and capacitance (capacitor). Series resonant circuits act in the line (low impedance with resonance) and parallel resonant circuits between the line and reference / ground (high impedance with resonance).
- two or more oscillating circuits coupled either electrically or magnetically. A slightly supercritical coupling is characteristic, which leads to the split of the resonance frequency into two maxima which are close together. A hat-shaped transfer function, which is usually desired, can thus be approximated well. Examples are the band filters of all classic intermediate frequency amplifiers in television and radio receivers based on the superhet principle, as well as filters using stripline technology (e.g. hairpin filters , see below).
- Active filters , such as Sallen-Key filters , contain active elements (amplifiers) and a feedback. You can achieve high filter slopes without coils.
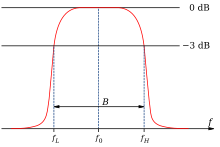
The pass band , which is represented by the transfer function , is characterized by the bandwidth B around the center frequency f 0 . The center frequency is defined as the geometric mean of f H and f L :
The bandwidth B of the filter is the difference between the upper and lower limit frequency ( f H and f L ). The cutoff frequencies are defined by reducing the level by 3 dB compared to the maximum value.
Bandpasses have at least a filter order of two. Bandpass filters with a symmetrical transfer function around the center frequency f 0 have an even filter order.
2nd order bandpass
The simplest bandpass with an oscillating circuit is a 2nd order bandpass, as it is sketched as an electrically passive filter in the adjacent figure. Second order bandpass filters have an edge steepness of 20 dB per decade apart from the pass band and the transfer function with the values of the components R , L and C is:
In general, the transfer function can also be expressed by a degree of damping D and the resonant angular frequency ω 0 . The relationship to the bandwidth B and the resonance frequency f 0 is:
Alternatively, the transfer function can also be given a quality factor Q :
be expressed. High quality factors Q result in narrow-band band filters.
Higher order bandpasses
Higher order bandpass filters have steeper filter edges towards the stop band and, in contrast to the 2nd order bandpass filters, can have a flatter course of the absolute frequency response in the pass band. The transfer function for a 4th order bandpass is, for example:
with the general coefficients a 1 , b 1 , b 2 and b 3 .
Areas of application
electronics
In electronics , continuous bandpass filters are used as active or passive filters at frequencies below about 10 MHz. Electrical bandpass filters can be expressed as a reaction-free combination of a high-pass and a low-pass , as in third- octave filters and octave filters , which have standardized transfer functions with very steep slopes. Typical components are capacitors , resistors and coils . With active bandpass filters in the low frequency range, filter properties are improved by additional operational amplifiers . The dimensioning can be based on the filter design of low-pass filters, the band-pass with an even filter order being formed by a low-pass-band-pass transformation .
If the signal was previously digitized by analog-to-digital converters , the digital signal processing methods offer very effective and economical methods, since bandpasses, like other filters, can also be implemented as time-discrete filters . The quantized filter coefficients for the digital bandpass filter can be obtained from the continuous-time, analog filter , for example, by the bilinear transformation .
In the high frequency range around 100 MHz, on the other hand, the phenomenon of resonance is used , because resonant circuits can - depending on their circuit - become high-resistance (parallel resonant circuit ) or low-resistance (series resonant circuit). Their properties are significantly exceeded by the smaller surface acoustic wave filters and quartz filters . The main application is frequency selection in heterodyne receivers at the intermediate frequency level . In elaborately designed receivers, several such band filters were each provided with an amplifier stage and connected in series in order to achieve a particularly high degree of selectivity.
In the microwave range , bandpass filters often consist of strip conductors or holes and slots in or between waveguides . Dielectric resonators are small and have very high quality factors .
speaker
A loudspeaker housing in which the loudspeaker has no direct coupling to the sound space is referred to as a bandpass loudspeaker . It cannot be seen from the outside, the entire sound is emitted through the "reflex opening (s)". Inside, the system usually consists of two chambers, at least one of which is designed as a bass reflex housing .
This design allows higher frequency components (mid and high range) to be filtered out without an electrical crossover. Such housings are used for pure bass reproduction .
optics
Bandpass filters for optical wavelengths are color filters . They often consist of interference filters and can have a very narrow band. Another adjustable, narrow-band optical bandpass is the monochromator .
literature
- Ulrich Tietze, Christoph Schenk: Semiconductor circuit technology . 12th edition. Springer, Berlin 2002, ISBN 3-540-42849-6 .
- BA Shenoi: Introduction to Digital Signal Processing and Filter Design . Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken, NJ 2006, ISBN 0-471-46482-1 .









