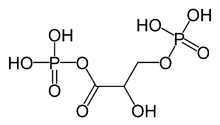
1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid
| Structural formula | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||
| Structural formula without stereochemistry | ||||||||||
| General | ||||||||||
| Non-proprietary name | Bisphosphoglycerate, disphosphoglycerate, Negelein -Ester | |||||||||
| other names |
|
|||||||||
| Molecular formula | C 3 H 8 O 10 P 2 | |||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| properties | ||||||||||
| Molar mass | 266.04 g mol −1 | |||||||||
| safety instructions | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | ||||||||||
1,3- Biphosphoglyceric acid or 1,3BPG ( 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate or 1,3-disphosphoglycerate ) is an organic molecule with a chain of three carbon atoms that occurs in the organism of living things. 1,3-Biphosphoglyceric acid occurs as a metabolic intermediate both in glycolysis in cell respiration and in the Calvin cycle in photosynthesis . 1,3BPG is an intermediate product between 3-phosphoglyceric acid and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate , during the fixation of CO 2 in photosynthesis. 1,3BPG is also the precursor molecule to 2,3-biphosphoglyceric acid . 1,3-Biphosphoglyceric acid was discovered in 1939 by Erwin Negelein (hence the name Negelein ester ).
Structure and biological role
1,3-Biphosphoglycerate is the anion of 1,3-Biphosphoglyceric acid that occurs in aqueous solutions . It is an oxidized glycerol that is phosphorylated via an ester bond and an anhydride bond . These functional groups give 1,3BPG important biological properties, such as the ability to phosphorylate ADP to ATP and thereby store energy.
In glycolysis
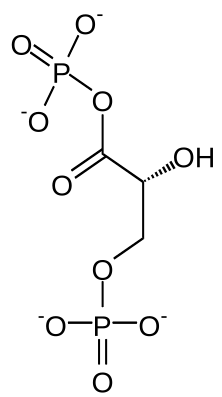
In glycolysis , 1,3BPG is an intermediate product in the production of energy from glucose .
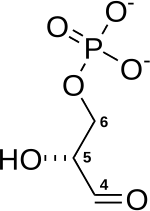
| Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1,3- bisphospho - D- glyceric acid | 3-phosphoglycerate kinase | 3- phospho - D- glyceric acid | ||
|
|

|
||||
| NAD + + P i | NADH + H + | ADP | ATP | |||

|

|
|||||
| NAD + + P i | NADH + H + | ADP | ATP | |||
| Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase | Phosphoglycerate kinase | |||||
In the Calvin cycle
In the Calvin cycle, 1,3BPG is formed analogously to glycolysis, only the reaction steps run in reverse order, NADPH is used as the electron donor instead of the electron acceptor NAD + and ATP is consumed instead of formed. The 1,3BPG comes from 3-phosphoglyceric acid in the Calvin cycle and is converted to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate , NADPH and phosphate through reduction by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase with NADPH . The ATP consumption is irreversible in the Calvin cycle.
In the oxygen release
In red blood cells is in Luebering-Rapoport pathway a byway of glycolysis, of about 20 percent of the 1,3BPG by the bisphosphoglycerate mutase the 2,3BPG formed. 2,3BPG is used in erythrocytes to increase the release of oxygen from hemoglobin . If there is a lack of oxygen, more 1,3BPG is produced through increased glycolysis and reduced cellular respiration and, as a result, more 2,3-BPG is formed, which increases the release by binding to hemoglobin.
literature
- Bruce Alberts, et al. : Molecular Biology of the Cell . Garland Science, New York 2001, ISBN 0-8153-4072-9 .
- William J. Germann, Stanfield, Cindy L .: Principles of Human Physiology . Benjamin Cummings, San Francisco 2002, ISBN 0-8053-6056-5 .
- Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Lubert Stryer : Biochemistry. 5th edition. Freeman, New York 2002, ISBN 978-0-7167-4684-3 , available online from the NCBI Bookshelf.
Web links
- 1,3BPG in glycolysis and fermentation (in English)
- Evidence in the Medical Dictionary for 1.3BPG (in English)
- 1,3BPG enzyme mechanism (in English)
Individual evidence
- ↑ This substance has either not yet been classified with regard to its hazardousness or a reliable and citable source has not yet been found.
- ↑ Erwin Negelein, Heinz Brömel: R-Diphosphoglyceric acid, its isolation and properties. In: Biochemical Journal . 303/1939. Springer, pp. 132-144.