Erwin Negelein
Erwin Negelein (born May 15, 1897 in Berlin ; † February 7, 1979 there ) was a German biochemist and cell biologist who worked as an employee of Otto Warburg and Karl Lohmann . From 1955 he worked as a professor at the Humboldt University in Berlin , then from 1961 to 1964 as director of the Institute for Cell Physiology of the German Academy of Sciences in Berlin . In particular, he investigated various enzymes involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates and amino acids , and in 1939 discovered the compound 1,3-diphosphoglycerate , an intermediate product of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, also known as the "Negelein ester" .
Life
Erwin Negelein was born in Berlin in 1897 as the son of a master carpenter . He initially trained as a mechanic and then from 1919 worked at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Cell Physiology in his hometown - headed by the later Nobel Prize winner Otto Warburg. After he had obtained his school-leaving certificate on Warburg's advice in 1927 , he completed part-time chemistry studies at the University of Berlin , which he completed with a doctorate in 1932 . Between 1920 and 1930 he had already published over 20 scientific publications together with Warburg , including papers on the Warburg hypothesis on the glucose metabolism of tumors . From 1932 to 1945 he was a research assistant at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Cell Physiology .
After the end of the Second World War , Erwin Negelein worked in Berlin-Buch at the Institute for Medicine and Biology of the German Academy of Sciences in Berlin, which later became the Academy of Sciences of the GDR . In the biochemistry department, he initially acted as deputy to the department head Karl Lohmann , and later took over the management of the cell physiology department. From 1955 he also worked as adjunct professor for physiological chemistry at the Humboldt University in Berlin. After the Buch Academy Institute was divided into several individual institutes in 1961, he became director of the newly established Institute for Cell Physiology . His successor in this function was Heinz Bielka from 1964 .
Erwin Negelein was married from 1921 and had a son and a daughter. He died in Berlin in 1979.
Scientific work
During his time at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Cell Physiology, Erwin Negelein was primarily concerned with the pure preparation of enzymes in the metabolism of carbohydrates and amino acids . This is how he succeeded in crystallizing the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and pyruvate kinase for the first time . In addition, he contributed to the elucidation of the structure and function of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP). During his time at the Academy Institutes in Berlin-Buch, he turned to in-vitro studies on the growth and metabolism of tumors and made fundamental contributions to the development of methods for testing the effectiveness of cytostatics .
Awards and memories
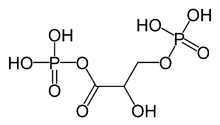
Erwin Negelein was awarded the Patriotic Order of Merit in bronze in 1962 and was made an honorary member of the Biochemical Society of the GDR in 1972. The Erwin-Negelein-Haus, named after him, reminds of him, a biotechnological laboratory building built in 1998 on the biomedical campus Berlin-Buch ( 52 ° 37 ′ 33.9 ″ N , 13 ° 30 ′ 4.8 ″ E, ), as well as a portrait bust of the sculptor Sabina Grzimek placed in front of the building . The substance he discovered, 1,3-diphosphoglycerate, an intermediate product of the carbohydrate metabolism in the context of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis , is also known as the "Negelein ester".
literature
- August W. Holldorf: Negelein, Erwin. In: New German Biography (NDB). Volume 19, Duncker & Humblot, Berlin 1999, ISBN 3-428-00200-8 , p. 31 f. ( Digitized version ).
- Biographies. Erwin Negelein. In: Heinz Bielka: History of the medical-biological institutes Berlin-Buch. Second edition. Springer-Verlag, Berlin and Heidelberg 2002, ISBN 978-3-540-42842-8 , pp. 177/178
Further publications
- Thomas Eichhorst: From Warburg's mechanic to professor: On the work of the biochemist Erwin Negelein (1897–1979). Dissertation at the Humboldt University of Berlin, Berlin 2000
Web links
- Literature by and about Erwin Negelein in the catalog of the German National Library
Individual evidence
- ↑ Erwin Negelein, Heinz Brömel: R-Diphosphoglyceric acid, its isolation and properties. In: Biochemical Journal . 303/1939. Springer, pp. 132-144
- ^ Brockhaus ABC Chemie , VEB FA Brockhaus Verlag Leipzig 1965, p. 929.
- ^ New Germany , October 6, 1962, p. 4
| personal data | |
|---|---|
| SURNAME | Negelein, Erwin |
| BRIEF DESCRIPTION | German biochemist and cell biologist |
| DATE OF BIRTH | May 15, 1897 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Berlin |
| DATE OF DEATH | 7th February 1979 |
| Place of death | Berlin |
